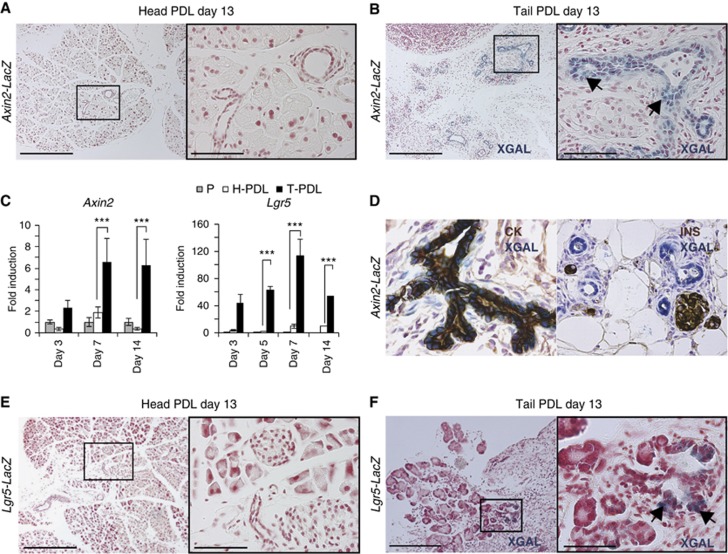
Figure 1.
Induction of Axin2 and Lgr5 expression upon damage on adult pancreas. (A, B) Axin2-LacZ induction in newly formed pancreatic ducts upon PDL. Axin2-LacZ mice (n=6) underwent PDL as explained in Materials and methods. Mice were sacrificed at the indicated time points and the non-ligated pancreatic tissue (Head-PDL) was separated from the ligated part (Tail-PDL). (A) Head-PDL and (B) Tail-PDL portion 13 days after injury. Arrows indicate XGAL-specific staining exclusively detected in the pancreatic ducts of the ligated pancreas. Scale bars 200 μm (A, B, left panels) and 50 μm (A, B, right panels). (C) qPCR analysis of Axin2 and Lgr5 mRNA in adult pancreas following PDL. Results are represented as mean±s.e.m. of at least three independent experiments. The Hprt housekeeping gene was used to normalize for differences in RNA input. Non-parametric Mann–Whitney test was used. ***P<0.0001. P, pancreas from a sham-operated mice; H-PDL, Head-PDL (non-affected area after PDL injury); T-PDL, Tail-PDL (affected area after PDL injury). (D) Representative image of a XGAL staining on an Axin2-LacZ pancreas after PDL, sections were co-stained either for pancytokeratin (CK), a duct cell marker, or for insulin (INS), an endocrine β-cell marker. XGAL staining (reflecting Axin2 expression) was detected exclusively in the pancreatic duct compartment. (E, F) Lgr5-LacZ induction in the ductal tree upon PDL. (E) Head PDL pancreas (n=6) do not show XGAL staining, indicating that Lgr5 is not expressed in non-injured pancreas. (F) Lgr5 reporter is detected (arrows) in the Tail-PDL portion of the ligated pancreas (n=6). Scale bars 200 μm (E, F, left panels) and 30 μm (E, F, right panels).