Abstract
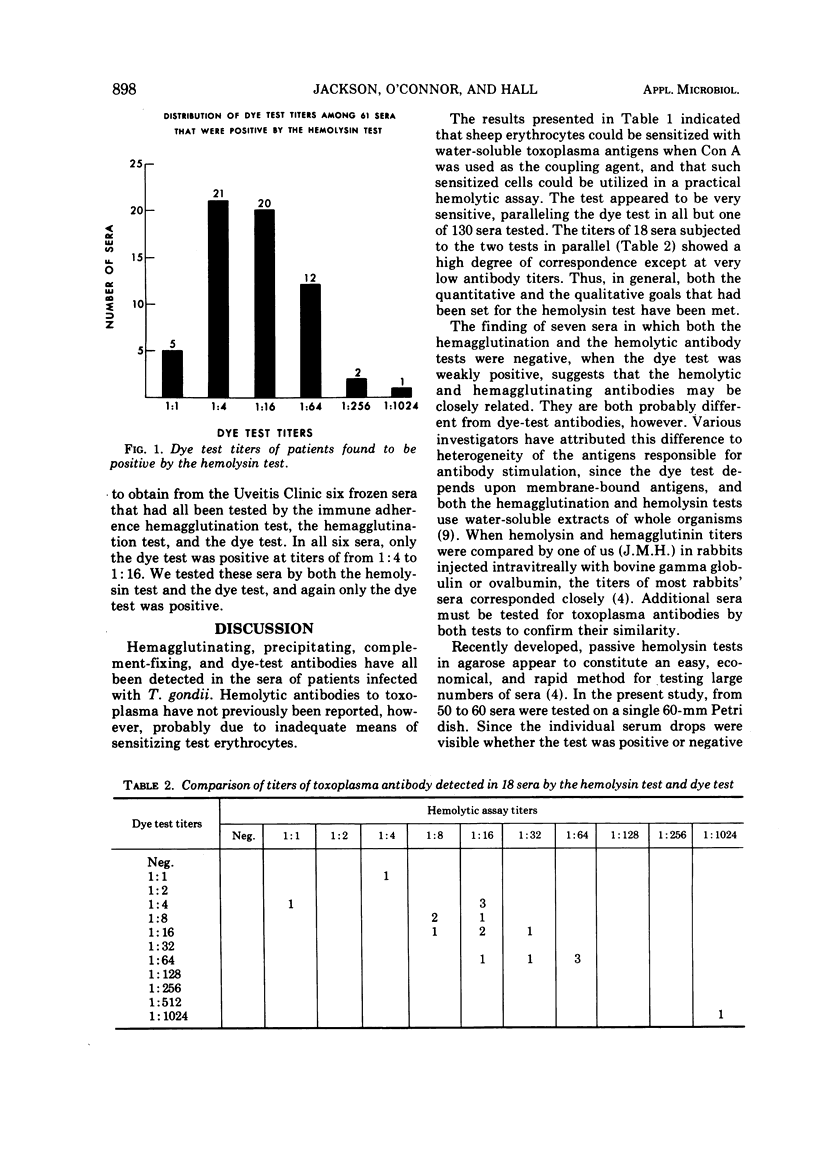
A plate hemolysin test was developed to screen serum specimens for the presence of toxoplasma antibodies. When we tested 130 sera by both this test and the standard toxoplasma dye test, we found the plate hemolysin test to be a rapid, sensitive, and economical method for detecting toxoplasma antibodies. In all but one instance it paralleled the dye test. A comparison of the results of testing six sera by the hemolysin, hemagglutination, and dye-test techniques suggested that the hemolytic antibodies were more closely related to hemagglutinating antibodies than to dye-test antibodies. We could not store sheep erythrocytes sensitized with toxoplasma lysate for more than 3 days without altering the sensitivity of the test. Concanavalin A proved to be an effective coupling agent for binding toxoplasma antigens to red-cell membranes, a quality attributed to its affinity for specific polysaccharide-combining sites.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DARRELL R. W., PIEPER S., Jr, KURLAND L. T., JACOBS L. CHORIORETINOPATHY AND TOXOPLASMOSIS, AN EPIDEMIOLOGIC STUDY ON A SOUTH PACIFIC ISLAND. Arch Ophthalmol. 1964 Jan;71:63–68. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1964.00970010079011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. J., Iyer R. N. Interaction of concanavalin A, a phytohemagglutinin, with model substrates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 May 26;121(1):197–200. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90374-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. J., Staub A. M. Interaction of concanavalin A with polysaccharides of Salmonellae. Immunochemistry. 1970 Mar;7(3):315–319. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(70)90170-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOGAN M. J., KIMURA S. J., O'CONNOR G. R. OCULAR TOXOPLASMOSIS. Arch Ophthalmol. 1964 Nov;72:592–600. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1964.00970020592003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hume O. S. Toxoplasmosis and pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1972 Nov 1;114(5):703–715. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(72)90853-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hübner K. F., Gengozian N. Critical variables of the Jerne plaque technique as applied to rodent antibody-forming systems responding to heterologous red cell antigens. J Immunol. 1969 Jan;102(1):155–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leon M. A., Young N. M. Concanavalin A: a reagent for sensitization of erythrocytes with glycoproteins and polysaccharides. J Immunol. 1970 Jun;104(6):1556–1557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunde M. N., Jacobs L. Differences in Toxoplasma dye test and hemagglutination antibodies shown by antigen fractionation. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1967 Jan;16(1):26–30. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1967.16.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nozik R. A., O'Connor G. R. Experimental toxoplasmic retinochoroiditis. Arch Ophthalmol. 1968 Apr;79(4):485–489. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1968.03850040487016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARK H. K. Toxoplasma hemagglutination test. Using alcohol-formalin fixed sensitized lyophilized erythrocytes. Arch Ophthalmol. 1961 Feb;65:184–191. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1961.01840020186006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabin A. B., Feldman H. A. Dyes as Microchemical Indicators of a New Immunity Phenomenon Affecting a Protozoon Parasite (Toxoplasma). Science. 1948 Dec 10;108(2815):660–663. doi: 10.1126/science.108.2815.660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner J. B., Howell S. F. Identification of Hemagglutinin of Jack Bean with Concanavalin A. J Bacteriol. 1936 Aug;32(2):227–237. doi: 10.1128/jb.32.2.227-237.1936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]