Abstract
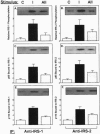
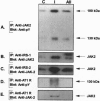
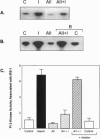
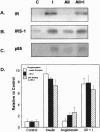
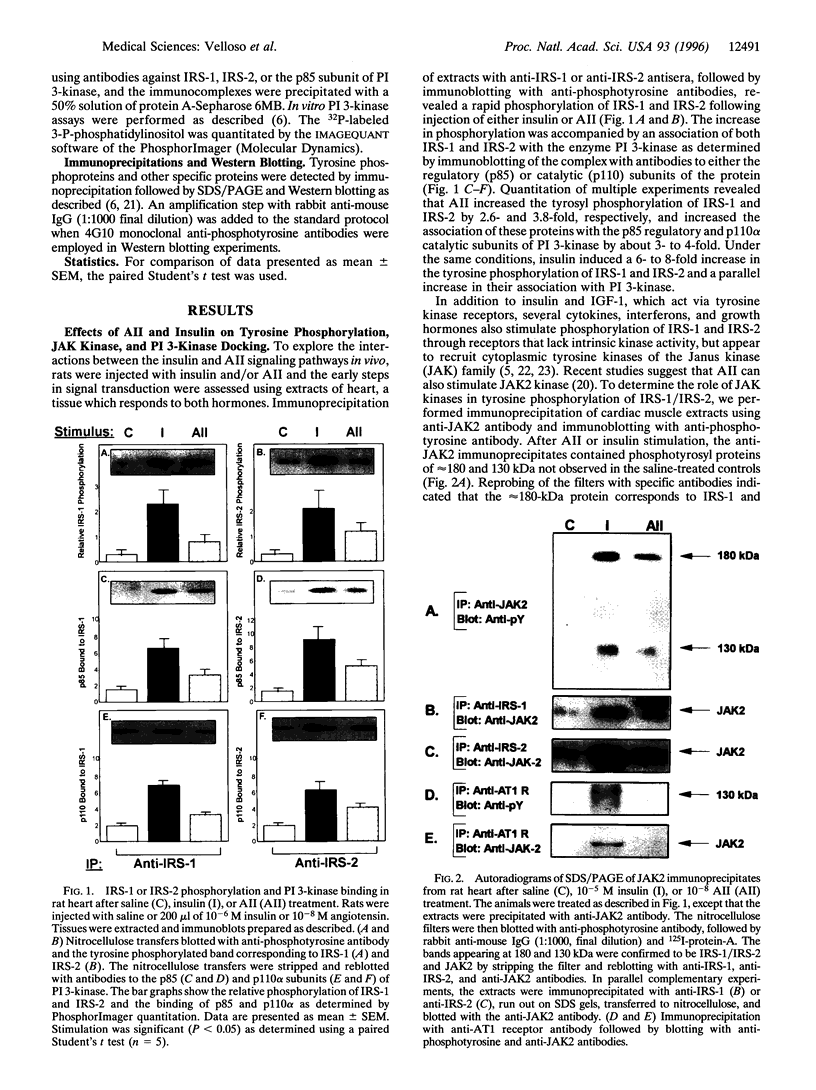
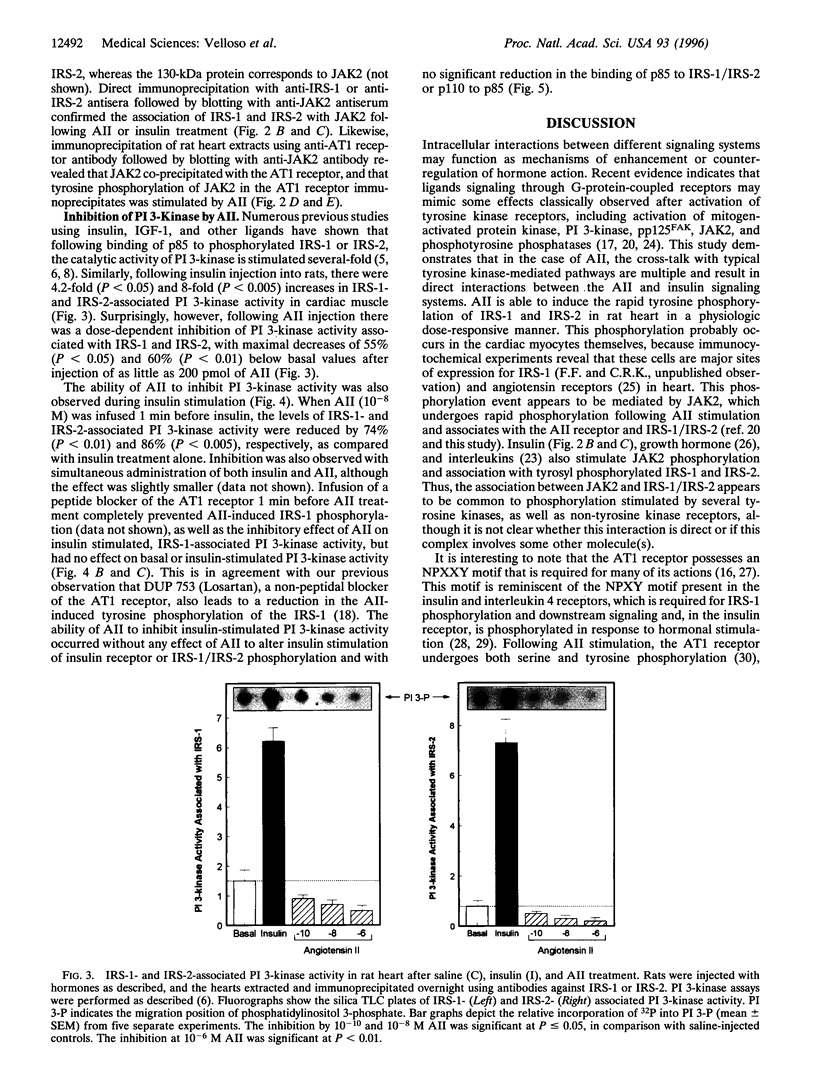
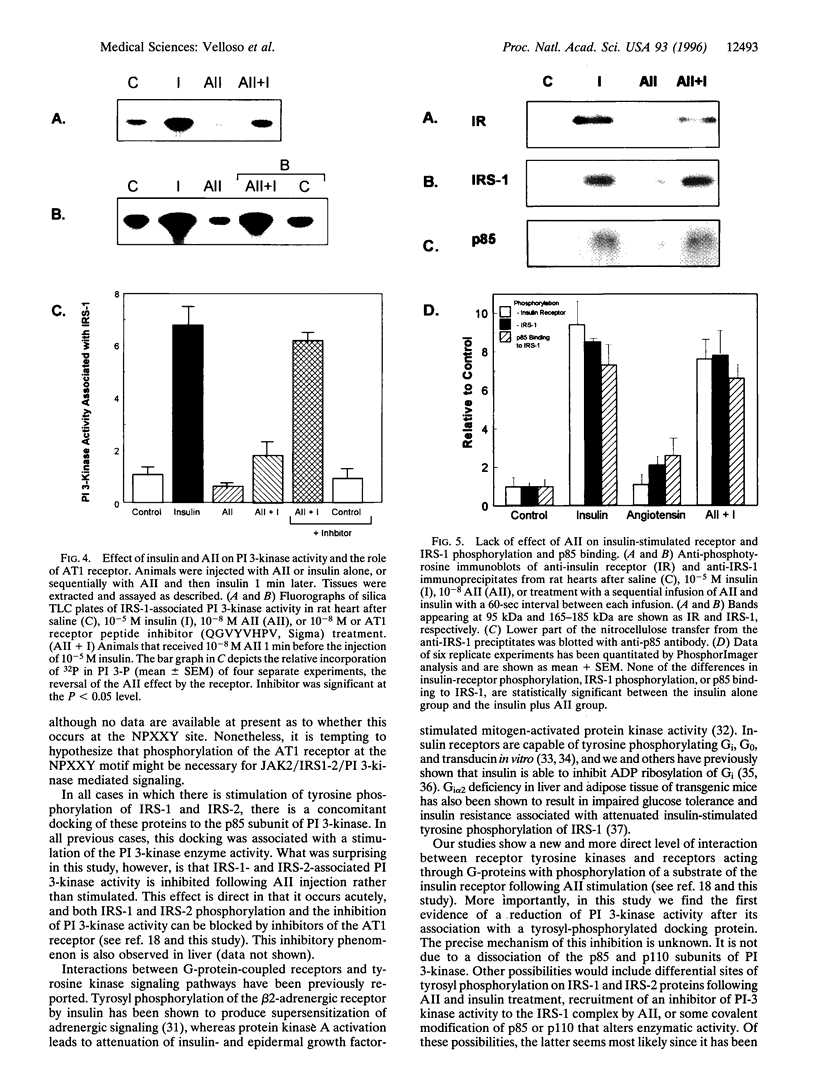
Angiotensin II (AII), acting via its G-protein linked receptor, is an important regulator of cardiac, vascular, and renal function. Following injection of AII into rats, we find that there is also a rapid tyrosine phosphorylation of the major insulin receptor substrates 1 and 2 (IRS-1 and IRS-2) in the heart. This phenomenon appears to involve JAK2 tyrosine kinase, which associates with the AT1 receptor and IRS-1/IRS-2 after AII stimulation. AII-induced phosphorylation leads to binding of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI 3-kinase) to IRS-1 and IRS-2; however, in contrast to other ligands, AII injection results in an acute inhibition of both basal and insulin-stimulated PI 3-kinase activity. The latter occurs without any reduction in insulin receptor or IRS phosphorylation or in the interaction of the p85 and p110 subunits of PI 3-kinase with each other or with IRS-1/IRS-2. These effects of AII are inhibited by AT1 receptor antagonists. Thus, there is direct cross-talk between insulin and AII signaling pathways at the level of both tyrosine phosphorylation and PI 3-kinase activation. These interactions may play an important role in the association of insulin resistance, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argetsinger L. S., Campbell G. S., Yang X., Witthuhn B. A., Silvennoinen O., Ihle J. N., Carter-Su C. Identification of JAK2 as a growth hormone receptor-associated tyrosine kinase. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90415-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argetsinger L. S., Hsu G. W., Myers M. G., Jr, Billestrup N., White M. F., Carter-Su C. Growth hormone, interferon-gamma, and leukemia inhibitory factor promoted tyrosyl phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate-1. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jun 16;270(24):14685–14692. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.24.14685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron A. D., Steinberg H. O., Chaker H., Leaming R., Johnson A., Brechtel G. Insulin-mediated skeletal muscle vasodilation contributes to both insulin sensitivity and responsiveness in lean humans. J Clin Invest. 1995 Aug;96(2):786–792. doi: 10.1172/JCI118124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrera-Hernandez G., Wanke I. E., Wong N. C. Effects of diabetes mellitus on hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 decrease albumin gene transcription. J Biol Chem. 1996 Apr 26;271(17):9969–9975. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.17.9969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braunwald E. ACE inhibitors--a cornerstone of the treatment of heart failure. N Engl J Med. 1991 Aug 1;325(5):351–353. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199108013250508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan T. A., Thawani H., Kades W., Modrall J. G., Weaver F. A., Laurel C., Poppiti R., Xiang A., Hsueh W. Angiotensin II increases glucose utilization during acute hyperinsulinemia via a hemodynamic mechanism. J Clin Invest. 1993 Aug;92(2):720–726. doi: 10.1172/JCI116642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caro J. F., Raju M. S., Caro M., Lynch C. J., Poulos J., Exton J. H., Thakkar J. K. Guanine nucleotide binding regulatory proteins in liver from obese humans with and without type II diabetes: evidence for altered "cross-talk" between the insulin receptor and Gi-proteins. J Cell Biochem. 1994 Mar;54(3):309–319. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240540307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheatham B., Vlahos C. J., Cheatham L., Wang L., Blenis J., Kahn C. R. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation is required for insulin stimulation of pp70 S6 kinase, DNA synthesis, and glucose transporter translocation. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;14(7):4902–4911. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.7.4902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung J., Grammer T. C., Lemon K. P., Kazlauskas A., Blenis J. PDGF- and insulin-dependent pp70S6k activation mediated by phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase. Nature. 1994 Jul 7;370(6484):71–75. doi: 10.1038/370071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhand R., Hiles I., Panayotou G., Roche S., Fry M. J., Gout I., Totty N. F., Truong O., Vicendo P., Yonezawa K. PI 3-kinase is a dual specificity enzyme: autoregulation by an intrinsic protein-serine kinase activity. EMBO J. 1994 Feb 1;13(3):522–533. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06290.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrannini E., Buzzigoli G., Bonadonna R., Giorico M. A., Oleggini M., Graziadei L., Pedrinelli R., Brandi L., Bevilacqua S. Insulin resistance in essential hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1987 Aug 6;317(6):350–357. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198708063170605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folli F., Saad M. J., Backer J. M., Kahn C. R. Insulin stimulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity and association with insulin receptor substrate 1 in liver and muscle of the intact rat. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22171–22177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke T. F., Yang S. I., Chan T. O., Datta K., Kazlauskas A., Morrison D. K., Kaplan D. R., Tsichlis P. N. The protein kinase encoded by the Akt proto-oncogene is a target of the PDGF-activated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Cell. 1995 Jun 2;81(5):727–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90534-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herings R. M., de Boer A., Stricker B. H., Leufkens H. G., Porsius A. Hypoglycaemia associated with use of inhibitors of angiotensin converting enzyme. Lancet. 1995 May 13;345(8959):1195–1198. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(95)91988-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunyady L., Bor M., Baukal A. J., Balla T., Catt K. J. A conserved NPLFY sequence contributes to agonist binding and signal transduction but is not an internalization signal for the type 1 angiotensin II receptor. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jul 14;270(28):16602–16609. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.28.16602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida Y., Kawahara Y., Tsuda T., Koide M., Yokoyama M. Involvement of MAP kinase activators in angiotensin II-induced activation of MAP kinases in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. FEBS Lett. 1992 Sep 21;310(1):41–45. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81142-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R. Diabetes. Causes of insulin resistance. Nature. 1995 Feb 2;373(6513):384–385. doi: 10.1038/373384a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kai H., Griendling K. K., Lassègue B., Ollerenshaw J. D., Runge M. S., Alexander R. W. Agonist-induced phosphorylation of the vascular type 1 angiotensin II receptor. Hypertension. 1994 Oct;24(4):523–527. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.24.4.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keegan A. D., Nelms K., White M., Wang L. M., Pierce J. H., Paul W. E. An IL-4 receptor region containing an insulin receptor motif is important for IL-4-mediated IRS-1 phosphorylation and cell growth. Cell. 1994 Mar 11;76(5):811–820. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90356-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K. L., Ruderman N. B. Insulin-stimulated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Association with a 185-kDa tyrosine-phosphorylated protein (IRS-1) and localization in a low density membrane vesicle. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):4391–4398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laporte S. A., Servant G., Richard D. E., Escher E., Guillemette G., Leduc R. The tyrosine within the NPXnY motif of the human angiotensin II type 1 receptor is involved in mediating signal transduction but is not essential for internalization. Mol Pharmacol. 1996 Jan;49(1):89–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leduc I., Meloche S. Angiotensin II stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of the focal adhesion-associated protein paxillin in aortic smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 3;270(9):4401–4404. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.9.4401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linseman D. A., Benjamin C. W., Jones D. A. Convergence of angiotensin II and platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling cascades in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1995 May 26;270(21):12563–12568. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.21.12563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrero M. B., Schieffer B., Paxton W. G., Heerdt L., Berk B. C., Delafontaine P., Bernstein K. E. Direct stimulation of Jak/STAT pathway by the angiotensin II AT1 receptor. Nature. 1995 May 18;375(6528):247–250. doi: 10.1038/375247a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moan A., Risanger T., Eide I., Kjeldsen S. E. The effect of angiotensin II receptor blockade on insulin sensitivity and sympathetic nervous system activity in primary hypertension. Blood Press. 1994 May;3(3):185–188. doi: 10.3109/08037059409102250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxham C. M., Malbon C. C. Insulin action impaired by deficiency of the G-protein subunit G ialpha2. Nature. 1996 Feb 29;379(6568):840–844. doi: 10.1038/379840a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mèndez R., Myers M. G., Jr, White M. F., Rhoads R. E. Stimulation of protein synthesis, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E phosphorylation, and PHAS-I phosphorylation by insulin requires insulin receptor substrate 1 and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Jun;16(6):2857–2864. doi: 10.1128/mcb.16.6.2857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. M., Houslay M. D., Milligan G., Siddle K. The insulin receptor tyrosyl kinase phosphorylates holomeric forms of the guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins Gi and Go. FEBS Lett. 1987 Feb 23;212(2):281–288. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81361-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothenberg P. L., Kahn C. R. Insulin inhibits pertussis toxin-catalyzed ADP-ribosylation of G-proteins. Evidence for a novel interaction between insulin receptors and G-proteins. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15546–15552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saad M. J., Folli F., Kahn C. R. Insulin and dexamethasone regulate insulin receptors, insulin receptor substrate-1, and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in Fao hepatoma cells. Endocrinology. 1995 Apr;136(4):1579–1588. doi: 10.1210/endo.136.4.7895667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saad M. J., Velloso L. A., Carvalho C. R. Angiotensin II induces tyrosine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate 1 and its association with phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in rat heart. Biochem J. 1995 Sep 15;310(Pt 3):741–744. doi: 10.1042/bj3100741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott A. L., Chang R. S., Lotti V. J., Siegl P. K. Cardiac angiotensin receptors: effects of selective angiotensin II receptor antagonists, DUP 753 and PD 121981, in rabbit heart. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Jun;261(3):931–935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Servant M. J., Giasson E., Meloche S. Inhibition of growth factor-induced protein synthesis by a selective MEK inhibitor in aortic smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jul 5;271(27):16047–16052. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.27.16047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sevetson B. R., Kong X., Lawrence J. C., Jr Increasing cAMP attenuates activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):10305–10309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd P. R., Navé B. T., Siddle K. Insulin stimulation of glycogen synthesis and glycogen synthase activity is blocked by wortmannin and rapamycin in 3T3-L1 adipocytes: evidence for the involvement of phosphoinositide 3-kinase and p70 ribosomal protein-S6 kinase. Biochem J. 1995 Jan 1;305(Pt 1):25–28. doi: 10.1042/bj3050025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoyanov B., Volinia S., Hanck T., Rubio I., Loubtchenkov M., Malek D., Stoyanova S., Vanhaesebroeck B., Dhand R., Nürnberg B. Cloning and characterization of a G protein-activated human phosphoinositide-3 kinase. Science. 1995 Aug 4;269(5224):690–693. doi: 10.1126/science.7624799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. J., Wang L. M., Zhang Y., Yenush L., Myers M. G., Jr, Glasheen E., Lane W. S., Pierce J. H., White M. F. Role of IRS-2 in insulin and cytokine signalling. Nature. 1995 Sep 14;377(6545):173–177. doi: 10.1038/377173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valiquette M., Parent S., Loisel T. P., Bouvier M. Mutation of tyrosine-141 inhibits insulin-promoted tyrosine phosphorylation and increased responsiveness of the human beta 2-adrenergic receptor. EMBO J. 1995 Nov 15;14(22):5542–5549. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00241.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Kahn C. R. The insulin signaling system. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Livingston J. N., Backer J. M., Lauris V., Dull T. J., Ullrich A., Kahn C. R. Mutation of the insulin receptor at tyrosine 960 inhibits signal transmission but does not affect its tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):641–649. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi K., Milarski K. L., Saltiel A. R., Pessin J. E. Protein-tyrosine-phosphatase SHPTP2 is a required positive effector for insulin downstream signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jan 31;92(3):664–668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.3.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin T., Keller S. R., Quelle F. W., Witthuhn B. A., Tsang M. L., Lienhard G. E., Ihle J. N., Yang Y. C. Interleukin-9 induces tyrosine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate-1 via JAK tyrosine kinases. J Biol Chem. 1995 Sep 1;270(35):20497–20502. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.35.20497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zavaroni I., Bonora E., Pagliara M., Dall'Aglio E., Luchetti L., Buonanno G., Bonati P. A., Bergonzani M., Gnudi L., Passeri M. Risk factors for coronary artery disease in healthy persons with hyperinsulinemia and normal glucose tolerance. N Engl J Med. 1989 Mar 16;320(11):702–706. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198903163201105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zick Y., Sagi-Eisenberg R., Pines M., Gierschik P., Spiegel A. M. Multisite phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of transducin by the insulin receptor kinase and protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9294–9297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]