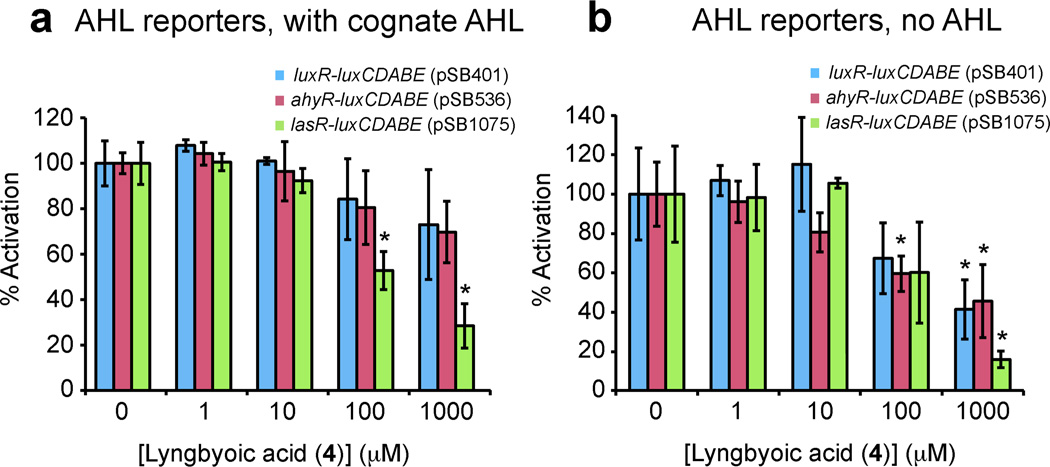
Figure 3.
Determination of inhibitory activity of compound 4 in luxCDABE reporter constructs expressed in E. coli (see Table S1, Supporting Information). (*) Indicates downregulation with statistical significance of P < 0.05 (t-test), compared with untreated controls, and error bars depict standard deviation. a) Effect of lyngbyoic acid (4) on luminescence of the reporter strains pSB401, pSB536 and pSB1075 in the presence of 3-oxo-C6-HSL, C4-HSL and 3-oxo-C12-HSL, respectively. Compound 4 and the appropriate cognate AHL were added to a 96-well plate and the solvent was allowed to dry off before 100 µL cultures of the appropriate reporter strain were added to each well. Plates were incubated for 6.5 h at 37 °C before fluorescence was measured. Results are expressed as % activation compared to control wells treated with cognate AHL alone (100%). Compound 4 was able to inhibit 3-oxo-C12-HSL mediated luminescence in pSB1075 and to a lesser extent in the other reporters. b) Effect of lyngbyoic acid (4) on background luminescence, in the absence of cognate AHL. The same protocol as for panel a) was used, except that cognate AHLs were not added to the plate. Results are expressed as % activation compared to untreated control (100). Compound 4 reduced background luminescence in all reporters.