Figure 8.
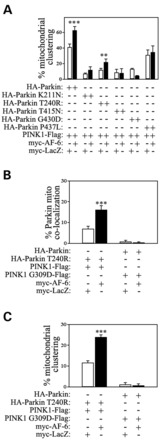
Effects of AF-6 on parkin and PINK1 familial disease-mutation deficiencies. (A) SH-SY5Y cells were transfected with the indicated Flag-parkin constructs, wild-type PINK1-HA and GFP-mito, and with either myc-AF-6 or myc-LacZ. Mitochondrial clustering was determined by analyzing GFP-mito using confocal microscopy. Error bars represent standard error of three independent experiments. **, ***Significantly different from LacZ control at P < 0.01 and 0.001, respectively. (B) SH-SY5Y cells were transfected with HA-parkin (wild-type or T240R), PINK1-Flag (wild-type or G309D) and GFP-mito, and with either myc-AF-6 or myc-LacZ. Parkin localization at the mitochondria was analyzed by immunocytochemistry with anti-HA and co-localization with GFP-mito analyzed by confocal microscopy. The graph shows the quantification of AF-6 effect in the translocation of parkin T240R. AF-6 did not rescue the deficiency in wild-type parkin translocation in the presence of PINK1 G309D disease-mutant. Error bars represent standard error of four independent experiments. ***Significantly different from LacZ control at P < 0.001. (C) Graph shows the quantification of AF-6 effect in the mitochondrial clustering induced by parkin T240R. AF-6 did not rescue the mitochondrial clustering deficiency in the presence of G309D mutant. SH-SY5Y cells were transfected and analyzed as in (B). Error bars represent standard error of four independent experiments. ***Significantly different from control at P < 0.001.
