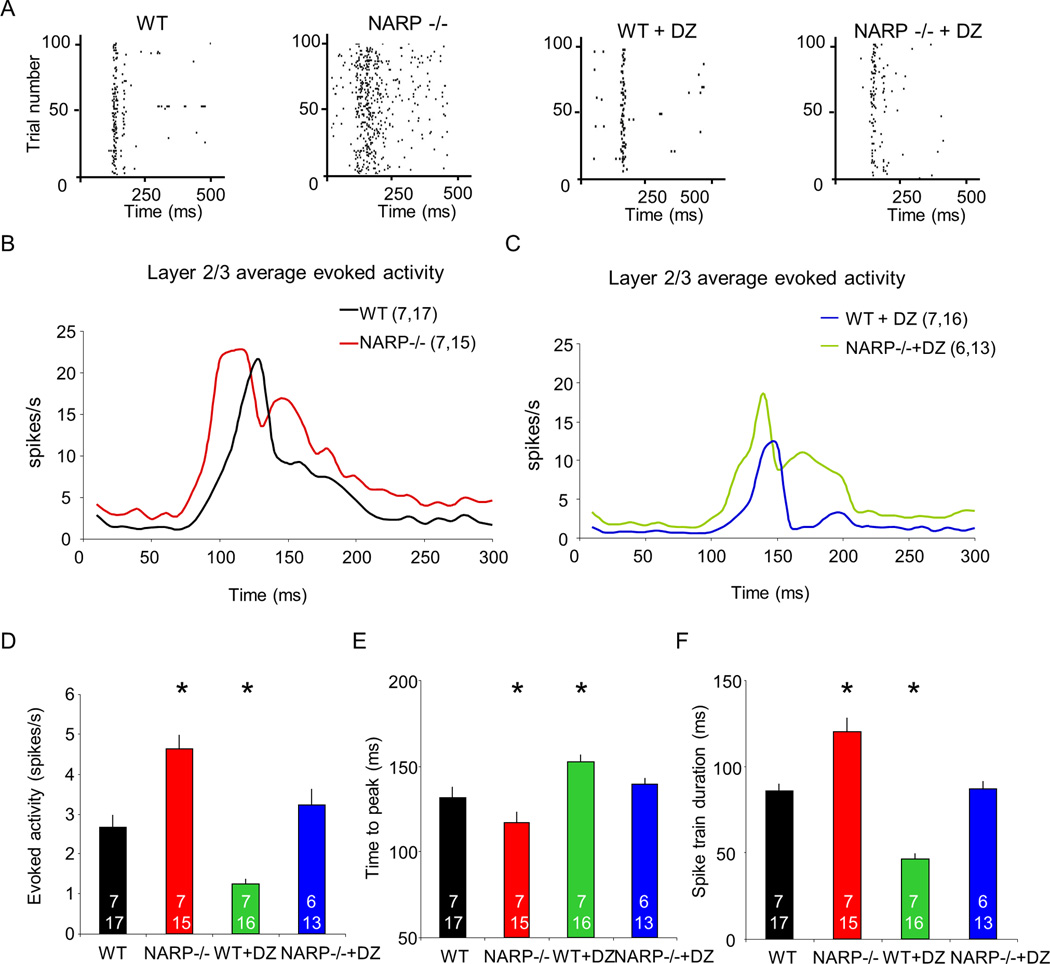
Fig 4. Enhanced neuronal excitability in layer 2/3 of NARP −/− visual cortex.
A. Representative raster plots of neuronal activity acquired in layer II/III of P28 visual cortex of wild type, NARP −/−, wild type + diazepam and NARP −/− + diazepam mice. In each case, activity is shown in response to visual stimulus in preferred orientation (1 Hz reversals of 0.04 cycles/degree; 100% contrast gratings, starting a time 0). B. Post-stimulus time histograms of average evoked activity of wild type and NARP −/− mice in response to visual stimulus in preferred orientation. Kruskal-Wallis H test, H=9.366, p=0.002. C. Post-stimulus time histograms of average evoked activity of wild type +diazepam and NARP −/− + diazepam in response to visual stimulus in preferred orientation. Kruskal-Wallis H test, H=21.01, p<0.001. D. Median evoked activity from layer II/III of P28 visual cortex of wild type, NARP −/−, wild type + diazepam and NARP −/− + diazepam mice. Kruskal-Wallis test, H(3)=37.812, p<0.001, *p<0.05 Mann-Whitney post hoc versus wild type controls. E. Time to peak evoked activity from layer II/III of P28 visual cortex of wild type, NARP −/−, wild type + diazepam and NARP −/− + diazepam. One way ANOVA, F3,57=8.449, p<0.001, *p<0.05 Bonferroni's post hoc versus wild type controls. F. Spike train duration from layer II/III of P28 visual cortex of wild type, NARP −/−, wild type + diazepam and NARP −/− + diazepam mice. One way ANOVA, F3,57=32.370, p<0.001, *p<0.05 Bonferroni's post hoc versus wild type controls.