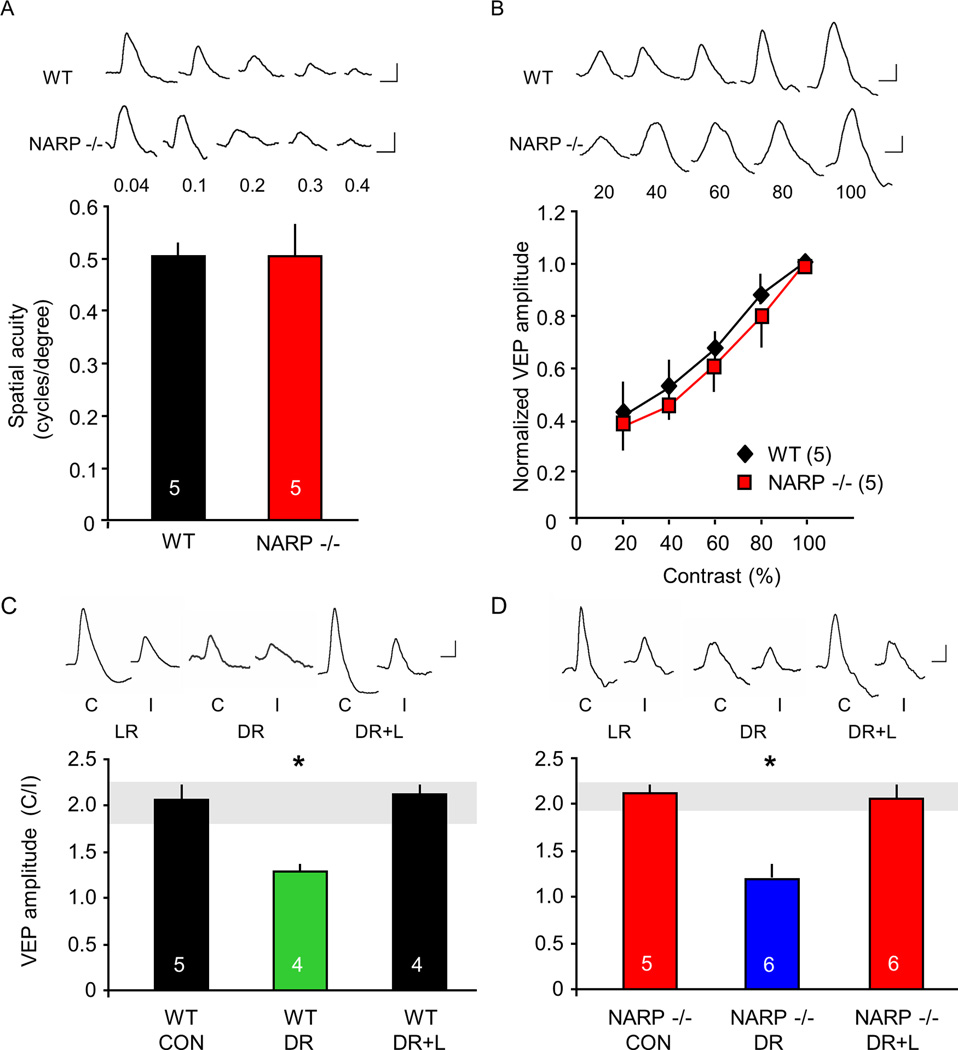
Fig 5. Normal vision in NARP −/− mice.
A. Comparable spatial acuity in NARP −/− mice and age-matched (P30) wild types. Spatial acuity is extrapolated from the linear regression of VEP amplitude versus spatial frequency of the visual stimulus. B. Comparable contrast sensitivity in NARP −/− mice and age-matched (P30) wild types. C. Two-fold VEP contralateral bias in P30 wild types (CON). Dark rearing (DR) from birth to P30 significantly inhibits the experience-dependent expression of VEP contralateral bias. Exposing dark-reared subjects to three days of normal lighted environment (DR+L) at P28 increases the VEP contralateral bias to the normal range (grey horizontal bar). One way ANOVA; F2,10=273.61, p<0.001. D. VEP contralateral bias is normal in P30 NARP −/− mice (CON). Dark rearing (DR) from birth to P30 significantly inhibits the experience-dependent expression of VEP contralateral bias. Exposing dark-reared subjects to three days of light (DR+L) at P28 increases VEP contralateral bias to the normal range (grey horizontal bar). One way ANOVA; F2,14=72.947, p<0.001; *p<0.01 Bonferroni’s post-hoc versus control. Inset: representative VEP waveforms. Scale bars: 50 ms, 50 µV.