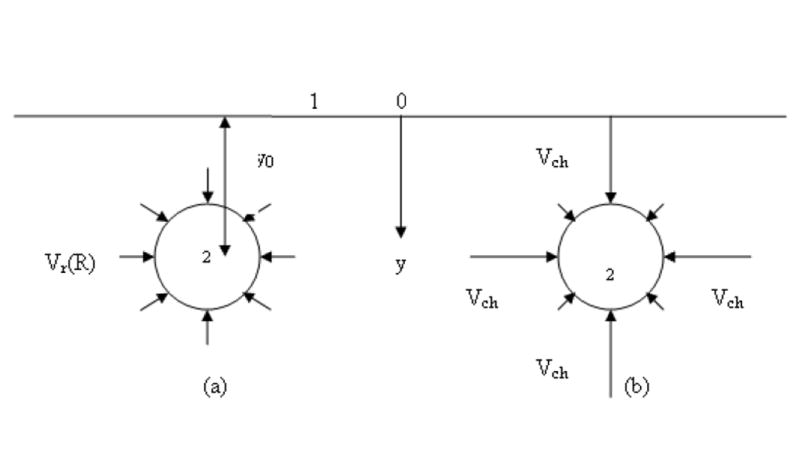
1 – a portion of squamous layer (epithelial barrier); 2 – cross-section of an initial lymph capillary (ILC). y
0is the shortest distance between 1 and 2. The length of arrows illustrates the velocity of interstitial fluid on the initial lymph capillary (ILC) surface caused by its soaking into the ILC.
-
(b)
uniform axial symmetrical velocity distribution (in the absence of channels).
-
(c)
velocity in channels, where the liquid contacting the initial lymph capillary wall is much larger than on the major portion of the wall.