Figure 2.
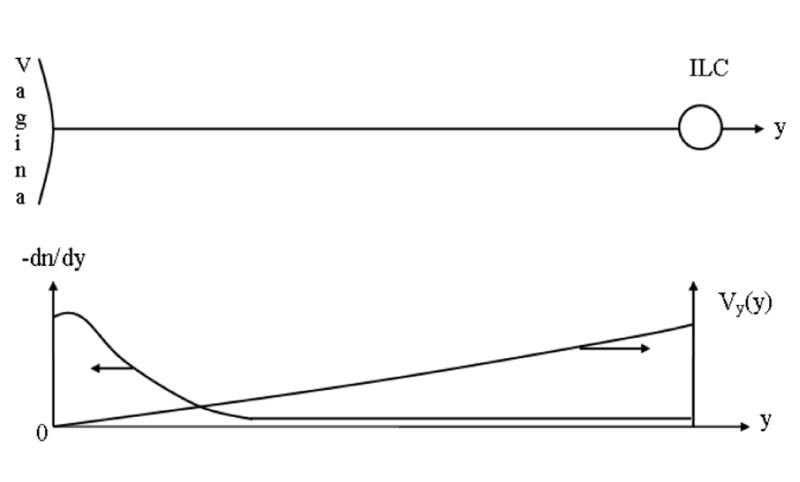
Convective diffusion of Qdots within the interstitium from foci in the epithelial barrier (EB) towards an initial lymph capillary (ILC). The Brownian diffusion predominates near the epithelial barrier (EB) because the interstitial fluid is immobilized in this zone. The velocity of interstitial fluid V increases with its approach to the initial lymph capillary (ILC), which causes the predomination of convection. The nanoparticle concentration n(y) is maximal near the exits of foci and decreases rapidly under the influence of increasing velocity Vy(y), which is the usual case in convective diffusion. Correspondingly, dn/dy decreases downstream with concomitant decrease in the diffusion flux.
