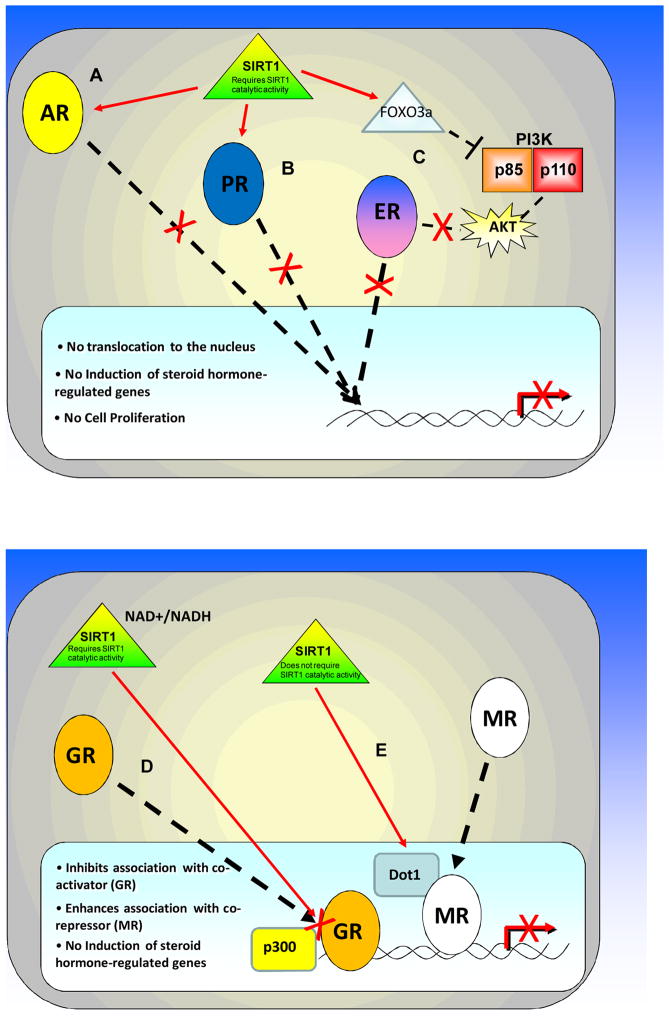
Figure 1. Model of SIRT1 regulation of steroid hormone receptor activity.
SIRT1 regulates individual steroid hormone receptors via different mechanisms. A) SIRT1 regulates the AR through direct deacetylation, thereby inhibiting AR activation and translocation and the transcription of AR-dependent genes. B) SIRT1 inhibits the PR by regulating the nucleo-cytoplasmic translocation of the receptor, and thereby the downstream activation of PR-regulated genes. C) SIRT1 regulates ERα by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT (p85/p110) pathway, possibly through FOXO3a. This inhibits the translocation of ERα from the cytoplasm to the nucleus, thus decreasing ERα binding to DNA and ERα-dependent gene transcription. D) The energy-sensing capabilities of SIRT1 regulate its effect on GR signaling. The cellular NAD/NADH ratio regulates SIRT1-mediated deacetylation of the GR and thus its ability to interact with the co-activator p300. E) SIRT1 regulates the MR by binding DOT1, thereby enhancing DOT1-mediated repression of MR-regulated genes. SIRT1 regulation of MR is independent of SIRT1 deacetylase activity.