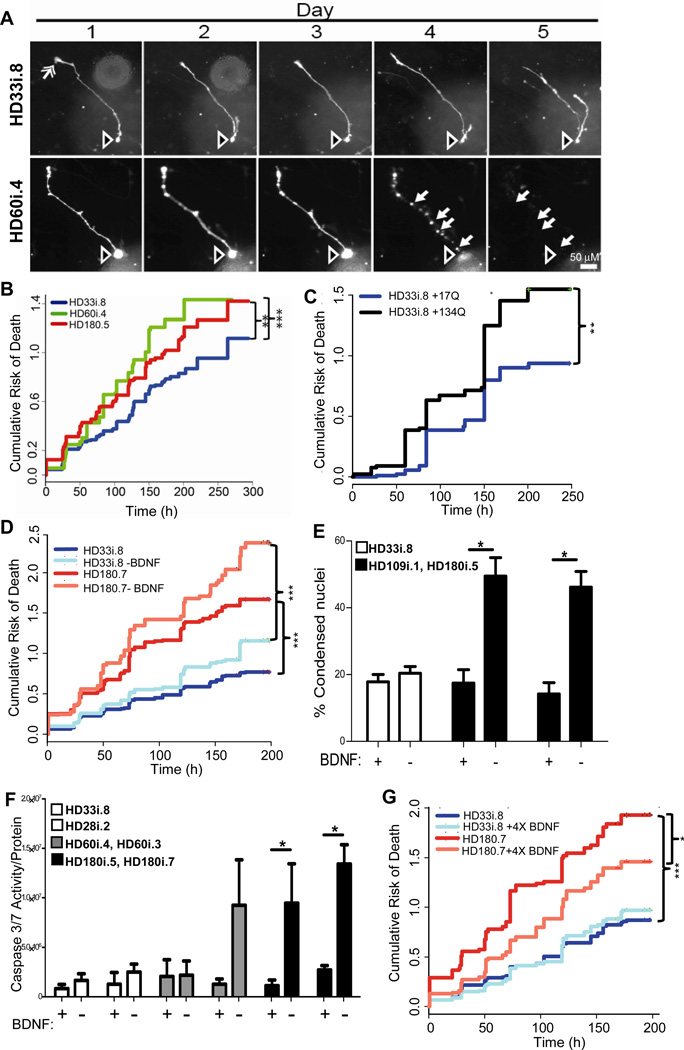
Figure 5. HD iPSCs Show Increased Risk of Death Over Time in Culture and Following Trophic Factor Withdrawal.
(A) Examples from a time series of images of two differentiated cells at day 35 from the HD33i.8 and HD60i.4 lines. Often cell bodies (hollow arrow, top and bottom rows) extend 1–3 processes, which are tipped by structures resembling growth cones (solid arrow, upper row, day 1). Degeneration and cell death were evident (bottom row, compare days 3–5) from the blebbing and retraction of neurites (closed arrows) and the loss of the cell soma (open arrow). Scale bar = 50 µm. (B) Kaplan-Meier analysis revealed that the cumulative risk of death was higher for the 180i.5 (hazard ratio is 1.4, p<0.01, n=337 cells) and the HD60i.4 (hazard ratio is 1.5, p<0.001, n=164 cells) lines compared to the HD33i.8 (n=248 cells) line. Total n=750 cells; 6 experiments for HD60i.4, 7 for HD180i.5 and 8 for HD33i.8.
(C) The cumulative risk of death is significantly increased in HD33i.8 cells over-expressing (by plasmid transfection) 134 CAG repeats (94 cells) compared to cells over-expressing 17 CAG repeats (92 cells). P<0.01, hazard ratio is 1.7, n=2 experiments. (D) The risk of death was significantly higher for the HD180i.7 line (195 cells) grown in BDNF compared to the HD33i.8 line (134 cells) grown in BDNF. Hazard ratio is 2.1 (p<0.001). After BDNF removal, the risk of death was significantly greater for the HD180i.7 line (156 cells) compared to the HD33i.8 line (n=191 cells), the hazard ratio is 2.56 (p<0.001). Removal of BDNF did not significantly increase the risk of death for the HD33i.8 and HD180i.7 lines compared to the lines grown in BDNF, however the increased risk of death for the HD180i.7 line after BDNF removal approached significance, p=0.08, hazard ratio=1.22, n=4 experiments. (E) BDNF was withdrawn for 48 hours, and cells were fixed and labeled with Hoechst. Quantifying condensed nuclei as a measure of cell toxicity showed that both HD109i.1 and HD180i.5 lines had significantly more cell death after BDNF withdrawal, whereas the HD33i.8 control line showed no change. ANOVA;* indicates p<0.01. (F) Quantifying caspase 3/7 after BDNF was withdrawn for 24 hours showed that both clones of the HD180i line demonstrated significant increases in caspase 3/7 activity. In addition to BDNF withdrawal, dbcAMP and VPA were removed from the medium as they increase endogenous BDNF transcription (Pruunsild et al., 2011). (G) Addition of 4X BDNF reduced the cumulative risk of death for HD180i.7. The risk of death is significantly less for the HD180i.7 line plus 4X BDNF (108 cells) compared to the HD180i.7 line alone (182 cells) (p<0.001). The hazard ratio is 0.67. There is no difference in the cumulative risk of death between the HD33i.8 line (208 cells) that received 4X BDNF (156 cells) p=0.43. The hazard ratio is 1.06, n=4 experiments.