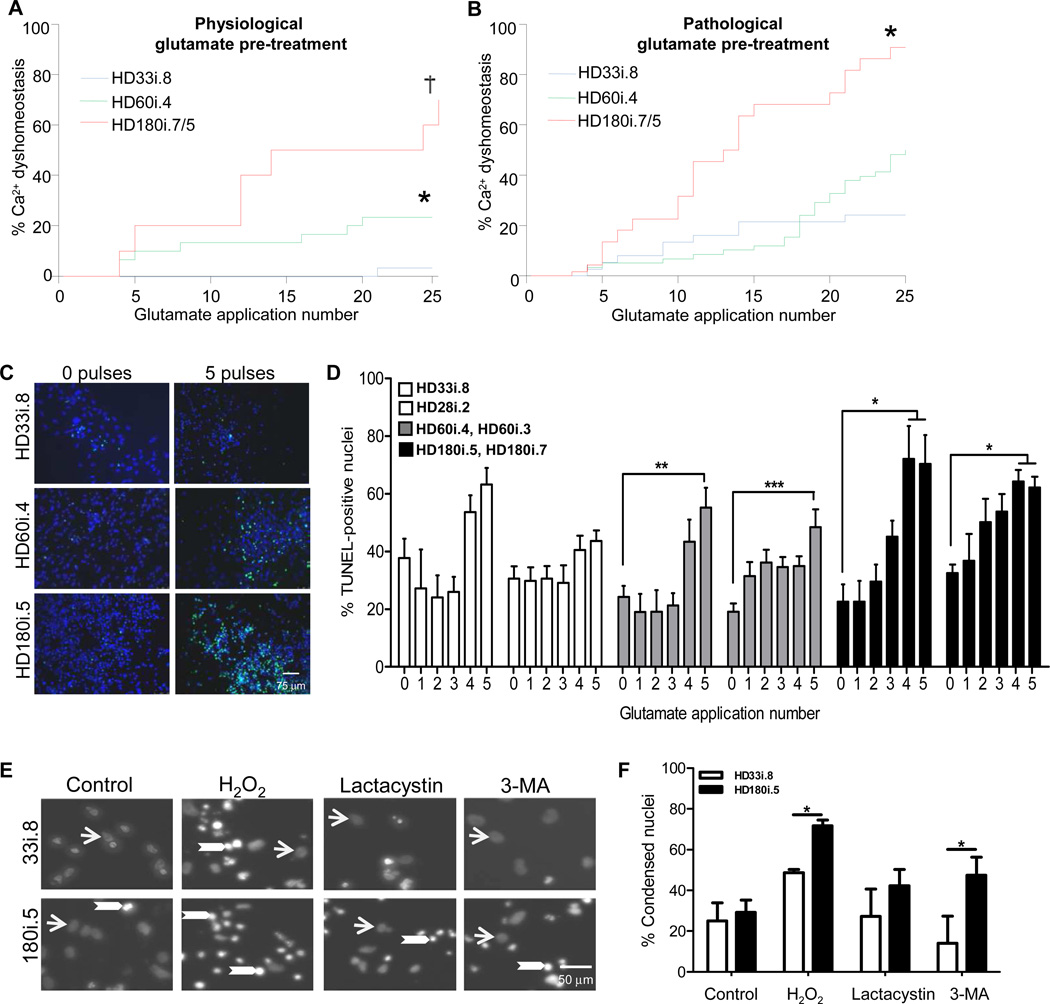
Figure 6. HD iPSCs have Increased Vulnerability to Stress and Toxicity.
(A) Using the short differentiation protocol, Ca2+ dysfunction was significantly elevated in the HD lines compared to the HD33i.8 line (* p< 0.02; † p <0.001). (B) As (A) except following a 14-day chronic pre-treatment with pathological glutamate (150 µM). Significantly different from *HD33i.8 p< 0.005; † HD60i.4 p< 0.0001. (C) Images demonstrate TUNEL-positive nuclei (green) and total nuclei (blue) in HD and control lines after exposure to no glutamate or 5 glutamate pulses. (D) HD iPSCs were differentiated for 56 days before repeated 30-minute pulses (0–5) with 50 µM glutamate. Cells were allowed to rest 24 hours before analyzing cell death. Compared to 0 glutamate pulses, TUNEL staining was significantly increased in both clones of the HD180i line after 4 or 5 glutamate pulses and in both clones of the HD60i line after 5 glutamate pulses. The control lines showed no significant increase after 5 pulses using a one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test. (E) Images demonstrate non-condensed nuclei (arrows) and bright condensed nuclei (arrowheads) in HD180i.5 and HD33i.8 differentiated iPSCs in either non-treated media or media treated with 300 µM H2O2, 10 µM lactacystin or 5 mM 3-MA. (F) Nuclear condensation assay shows enhanced toxicity of HD180i.5 cells compared to control HD33i.8 cells upon treatment with H2O2 or 3-MA.
*Significantly different (p<0.05).