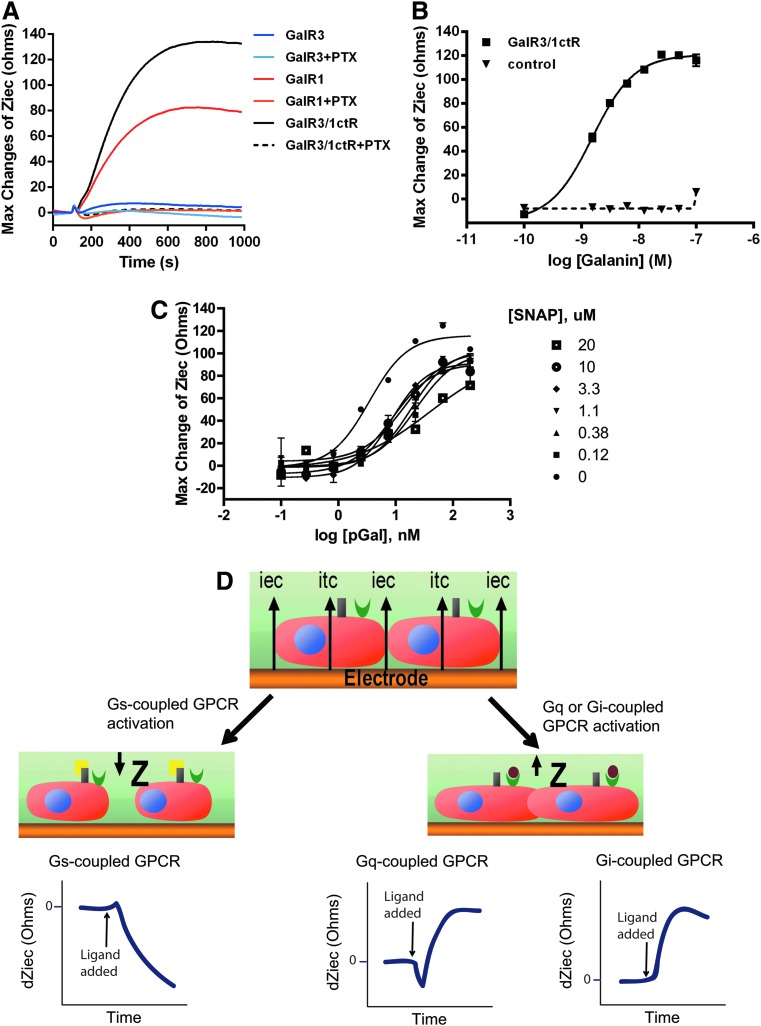
Fig. 4.
Cellular dielectric spectroscopy. (A) Time-dependent cellular dielectric spectroscopy (CDS) profiles induced by porcine galanin in HEK293-CNG cells expressing either GalR3, GalR1, or the Gal3/1ctR chimera. After 90 s of baseline read, 50 nM of porcine galanin was added and responses were collected for 1000 s. Plotted are individual data points collected every 2 s, each trace is a representative of three separate experiments. Pretreatment with pertussis toxin (PTX; 0.1 μg/mL) inhibited galanin-induced increase in cellular impedance observed in cells expressing the GalR1 and the Gal3/1ctR chimera. (B) HEK293-CNG-Gal3/1ctR cells (■) were treated with a range of porcine galanin concentrations and impedance values were exported at t=600 s. CRCs yielded an EC50 value of 1.5 nM. No response was observed in HEK293-CNG cells (control, ▼) (C) HEK293-CNG-Gal3/1ctR cells were treated with a range of porcine galanin concentrations in the presence of the indicated concentrations of SNAP37889 (SNAP) and impedance values were exported at t=600 s. Addition of SNAP37889 resulted in a concentration-dependent right shift of galanin CRC. In (B) and (C), data presented are means±SEM of triplicate wells (n=3). (D) Principle of Cellkey system. A voltage is applied at a number of frequencies. At low frequencies the voltage induces extracellular currents (iec) that pass around the cells, whereas at high frequency they induce transcellular current (itc). Changes in impedance are reported kinetically for each well allowing time-dependent traces in response to ligand to be plotted, such as in (A). Activation of a Gq-coupled receptor or a Gi-coupled receptor leads to an increase in actin polymerization and will cause cells to move closer to the electrode and to one another generating an increase in impedance. In contrast, activation of a Gs-coupled receptor results in actin depolymerization and will cause cells to move away from the electrode and to one another generating a decrease in impedance. Thus, the time-dependent response profiles are indicative of Gi, Gq, or Gs coupling. Alternatively, impedance at a single time point can be exported from each well and plotted against a range of ligand concentrations to generate dose response curves as in (B) and (C).