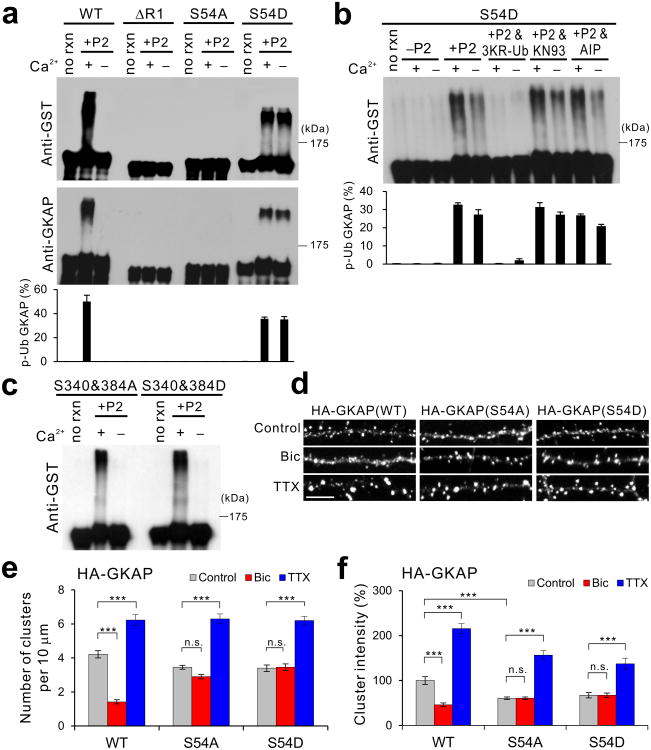
Figure 5.
Phosphorylation of Ser-54 in GKAP induces poly-ubiquitination and removal of GKAP from synapses. (a) In vitro ubiquitination of GST fusion proteins of GKAP WT, ΔR1, S54A, and S54D. Top two panels show representative results and quantification from triplicate experiments is shown at the bottom. Full-length blots are presented in Supplementary Figure 13. (b) Effect of Ca2+, 3KR-Ub, and CaMKII inhibitors (KN93 and AIP) on the in vitro ubiquitination of S54D mutant. (c) Normal Ca2+-dependent in vitro ubiquitination of GST fusion proteins of S340&384A and S340&384D mutants. (d-f) Activity-dependent turnover of S54A and S54D mutant in hippocampal neurons. Hippocampal neurons (14 DIV) were transfected with either HA-tagged WT, S54A, or S54D GKAP. Neurons were then treated with either Bic (40 μM) or TTX (2 μM) at 1 d post-transfection, and incubated further 36 h before fixation and immuno-staining for HA staining. (d) Representative images. Scale bar, 5 μm. (e) Quantification of HA cluster density. (f) Quantification of HA cluster intensity, normalized to WT control levels. n > 20 per condition. *** P < 0.001, ** P < 0.01, n.s., not significant. Error bars represent s.e.m.