Figure 1. C-kit+ cells are expressed in neonatal rat kidney and can be isolated by FACS.
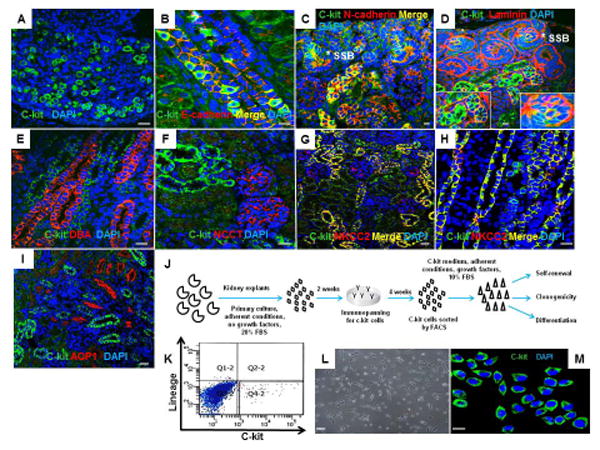
(A) C-kit+ cells in the renal papilla.
(B,C) C-kit+ cells in the medullary rays and nephrogenic cortex exhibiting co-localization with E-cadherin and N-cadherin, respectively.(*) represents S-shaped bodies (SSB).
(D) Section of the nephrogenic cortex costained for c-kit and laminin in SSB (*) and tubules. Insets show regions at higher magnification.
(E,F) C-kit+ cells did not stain for Dolichos biflorus agglutinin (DBA) or Na-Cl co-transporter (NCCT), respectively.
(G,H) Section of the nephrogenic cortex and medulla costained for c-kit and Na-K-2Cl co-transporter (NKCC2) in the thick ascending limb of Henle's loop.
(I) C-kit+ cells did not stain for aquaporin-1 (AQP1).
(J) Schematic of the experimental procedure for c-kit isolation from neonatal rat kidneys.
(K) Isolation of c-kit+/Lin− cells by FACS in the quadrant Q4-2 with depletion of lineage cells.
(L) C-kit+/Lin- cells in monolayer culture on plastic after sorting.
(M) Sorted cells were positive for the c-kit receptor.
Cell nuclei are stained blue with DAPI. Scale bars represent 20μm (A-I, M) and 50 μm (L).
