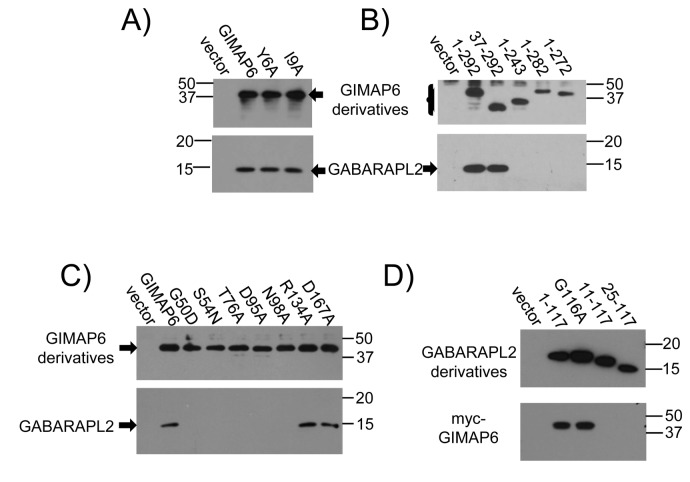
Figure 3. Identification of the domains of GIMAP6 and GABARAPL2 required for their interaction.
Panels A-C) HEK293T cells were transfected with 10µg wild-type GIMAP6 or the indicated mutated derivatives in plasmid pcDNA3Biot1His6iresBirA. Biotinylated and associated proteins were recovered by streptavidin-agarose affinity chromatography 48 h after transfection. Western blots of the recovered proteins were probed with HRP-conjugated streptavidin (to show the GIMAP6 proteins) or rat monoclonal antibody MAC446 to GABARAPL2 followed by an HRP-conjugated goat F(ab’)2 fragment anti-rat IgG. Panel A) GIMAP6 compared with mutations of the putative AIM motif in GIMAP6. Panel B) GIMAP6 compared with N- and C-terminal mutants of the protein as indicated. In panel B, 1-292 corresponds to full-length GIMAP6. Panel C) Mutations within the GTPase domain of GIMAP6 as indicated. Panel D) HEK293T cells were transfected with a plasmid encoding myc-GIMAP6 together with plasmids encoding biotinylated forms of GABARAPL2 as indicated. Cell lysates were prepared and biotinylated and associated proteins recovered by streptavidin-agarose affinity chromatography. Western blots were probed with HRP-conjugated streptavidin (to show the GABARAPL2 proteins) or an anti-myc monoclonal antibody 9E10 followed by an HRP-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG to detect myc-tagged GIMAP6. The wild-type protein is represented by 1-117. Results in all four panels are representative of data obtained from three independent experiments.