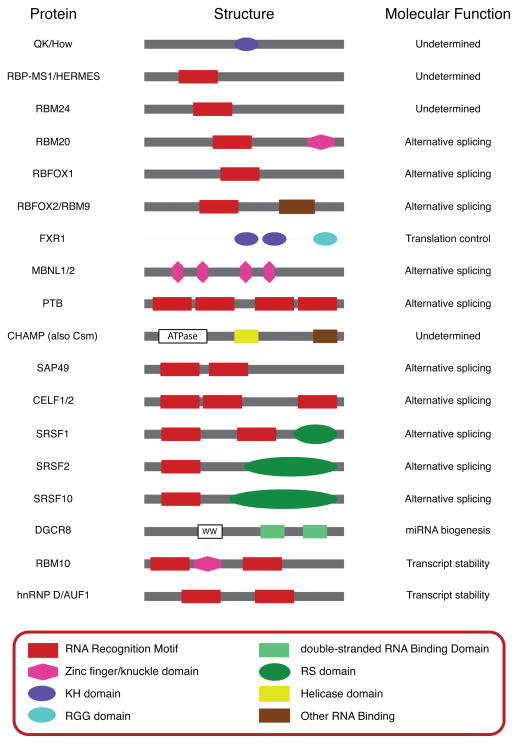
Figure 3. Domain structure of RNA binding proteins implicated in regulation of heart development.
Schematic representations of the type and position of important domains within the RNA binding proteins described in this review are shown. RNA binding domains and other domains characteristic of these RNA binding protein families are shown in color; other conserved domains are shown in black and white. Proteins and domains are not drawn to scale. Molecular functions of these RNA binding proteins within the heart are indicated, if known; additional functions of these proteins that have been demonstrated in other tissue types are not shown. The domain structures of these proteins are highly conserved across vertebrate species, and the depicted structures represent all homologs described in the text. Note that the structure of QK/How is conserved from human to fly, whereas to date CHAMP/Csm has only been described in mammals.