Figure 3. Substrate binding-induced perturbation centrality changes mark important residues of E. coli Met-tRNA synthetase.
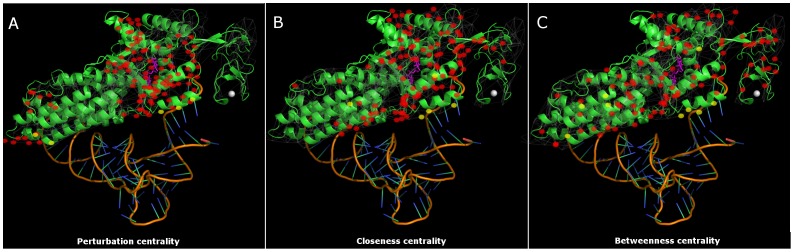
Protein structure networks of the substrate-free and substrate-bound forms of E. coli Met-tRNA synthetase protein were generated as described in the Supplementary Methods of Text S1. Perturbation centralities and the underlying protein structure network of Met-tRNA synthetase were calculated and visualized by the Turbine program as described in Methods, and were overlaid on the 3D image of the substrate-bound form of the protein (and its tRNAMet complex) generated with PyMOL [58] using ray-tracing. The bottoms of the images show the structure of tRNAMet. The purple molecule in the middle of the protein structure is the substrate Met-AMP marking the active site of the enzyme, the white sphere on the right is the Zn2+ ion. Red signs of Panels A, B and C mark amino acids having the highest increase of perturbation, closeness and betweenness centralities (top 20%) of the substrate-bound form compared to the substrate-free form, respectively. Yellow signs mark those contact amino acids, which are directly bound to the tRNAMet, evidenced by an atomic distance of less than 4.5Å between any atom of the residue and the tRNAMet, excluding hydrogens. To avoid overcrowding the image, only those contact amino acids are shown, which have a high increase of their centrality. A separate image showing all tRNAMet-binding amino acids is shown in Figure S9 of Text S1. Note that red-labeled amino acids having the largest increase of perturbation centrality upon substrate binding (Panel A) are clustered around the active site and around both tRNA-binding sites, thus successfully discriminate all important parts of the protein. Amino acids showing the highest change in closeness centrality (Panel B) are smeared around the active site (which also occurs to be near the geometric center of the protein). Amino acids showing the highest change in betweenness centrality (Panel C) are scattered all around the protein.
