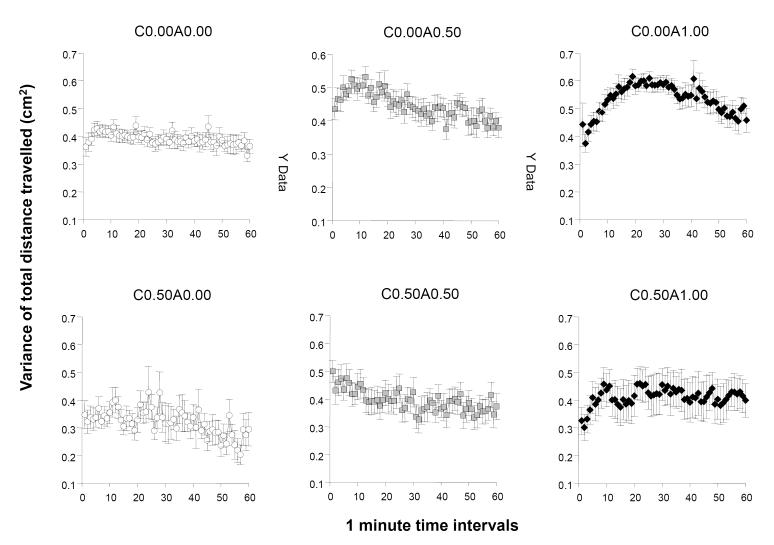
Figure 2.
The temporal trajectory of the within individual variance of total distance moved measured during a one hour long recording session is dependent upon the concentration of ethanol administered acutely during the session and on whether the fish were chronically pre-exposed to ethanol before. Note that this variance reflects the moment to moment changes in the speed with which the particular fish moved and thus increasing variance means less consistent swimming speed whereas decreasing variance means more steady swimming speed. Mean + S.E.M. are shown for 1-minute intervals of the recording session. The treatment conditions (group designations) are shown above the graphs. The values following the letter ‘C’ represent the concentration of ethanol (expressed as ethanol/water vol/vol %) employed during the chronic pre-treatment period (0.00 representing control and 0.50 the chronic ethanol exposed fish). The values following the letter ‘A’ represent the concentration of ethanol employed during the acute exposure, i.e. the behavioural recording, session (0.00 representing control, and 0.50 and 1.00 the corresponding acute ethanol exposed fish). Sample sizes (n) were as follows: C0.00A0.00 = 14; C0.00A0.50 = 13; C0.00A1.00 = 18; C0.50A0.00 = 13; C0.50A0.50 = 16; C0.50A1.00 = 10. Note the elevated activity in the group of fish acutely exposed to the intermediate concentration of ethanol (C0.00A0.50) as compared to control. Also note the inverted U-shaped temporal trajectory with an initially rising variance and subsequent falling variance in the highest acute concentration group (C0.00A1.00). Last observe the attenuation of the rising and falling phase and also the blunted overall increase of variance in the fish that were chronically pre-treated with ethanol and subsequently exposed to the highest ethanol dose acutely (C0.50A1.00 vs. C0.00A1.00). For details of statistical analysis and other group differences see Results.