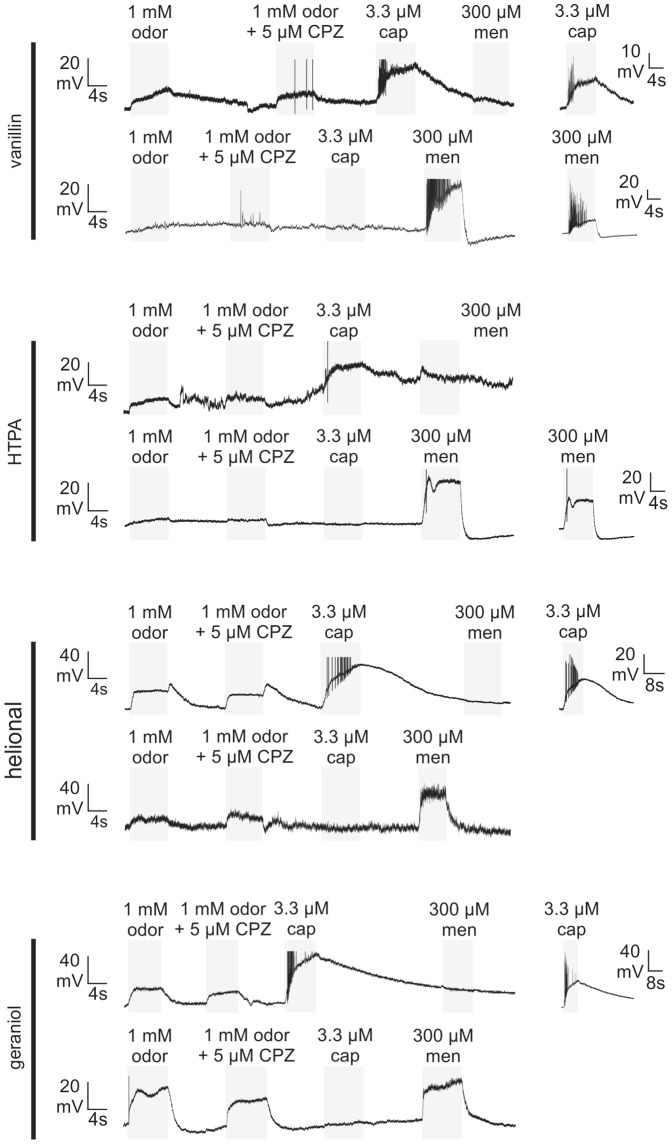
Figure 3. CC recording of cultured TG neurons stimulated with odorants in the presence and absence of CPZ.
Exemplary CC recordings from cultured TG neurons upon stimulation with vanillin, HTPA, helional, and geraniol alone and with CPZ. Membrane potential changes and RMP of recorded neurons upon stimulation with: vanillincap-sensitive: RMP: −45 mV; vanillin: Δ10 mV, vanillin+CPZ: Δ7 mV, cap: Δ20 mV, men: Δ0 mV; vanillinmen-sensitive: RMP: −62 mV; vanillin: Δ0 mV, vanillin+CPZ: Δ0 mV, cap: Δ0 mV, men: Δ29,5 mV; HTPAcap-sensitive; RMP: −67 mV; HTPA: Δ14.6 mV, HTPA+CPZ: Δ10.3 mV, cap: Δ27.5 mV, Δ2.6 mV; HTPAmen-sensitive; RMP: −61 mV; HTPA: Δ6.3 mV, Δ3.7 mV, cap: 0 mV, men: Δ31.4 mV; helionalcap-sensitive: RMP: −73 mV; helional: Δ29.1 mV, helional+CPZ: Δ22 mV, cap Δ67 mV, men: 0 mV; helionalmen-sensitive: RMP: −50 mV; helional Δ7.2 mV, helional+CPZ: Δ7.8 mV, cap: Δ0 mV; men: Δ25 mV; geraniolcap-sensitive: RMP: −67 mV; geraniol: Δ18 mV, geraniol+CPZ: Δ14 mV, cap: Δ53 mV, men Δ0 mV; geraniolmen-sensitive: RMP: −60 mV; geraniol: Δ17.6 mV, geraniol+CPZ: Δ14.5 mV, cap: Δ2 mV; men: Δ23 mV. Capsaicin- and menthol-evoked action potentials were cut at −30 mV (vanillin), −20 mV (HTPA), 0 mV (helional), and at −10 mV (geraniol). Stimulus applications are indicated by highlighted (gray) regions.