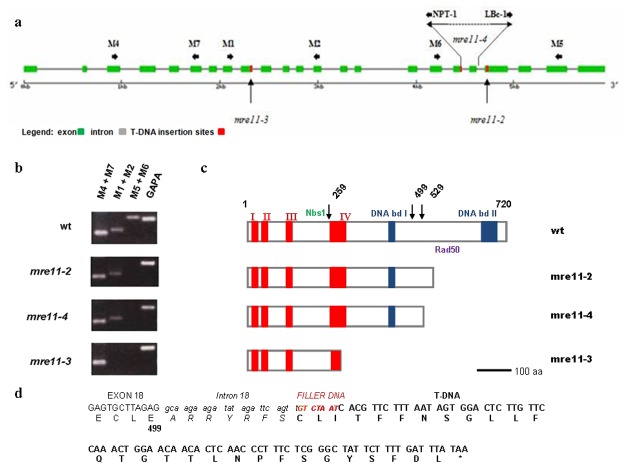
Figure 1. Molecular analysis and the effect of the T-DNA insertion in mre11 mutant lines.
a) Schematic representation of the mre11-4 allele with the T-DNA disruption located in the 18th intron (right border, NPT-1) and the left border (LBc-1) oriented toward 3´ end of the MRE11 gene. Vertical arrows indicate the T-DNA insertion sites for mre11-2 and mre11-3 alleles, previously characterized [21,35]. Green boxes represent exons. MRE11 gene specific primers are shown by short horizontal arrows. (b) Reverse transcriptase (RT)-PCR of MRE11 transcripts in wild-type and three mre11 mutants. The full-length transcripts were not produced in the three mre11 mutants. Primers spanning different regions of MRE11 transcripts used in the second round of RT-PCR are indicated at the top of each column. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase A (GAPA) was used as control for cDNA amount and quality. c) Schematic representation of the predicted full-length MRE11 protein (wt) and putative truncated MRE11 proteins: mre11-3 mutant lacks 461 amino acids, mre11-4 lacks 221 amino acids and mre11-2 lacks 191 amino acids. Arrows indicate the T-DNA disruption sites of the MRE11 gene with respect to the full-length protein. The various putative protein domains are marked according to [8,36]; the phosphoesterase motifs (I to IV) with red boxes and two DNA binding domains (blue boxes) as well as the regions important for NBS1 and RAD50 interaction. Ideograms are drawn roughly in scale. Scale bars indicate 100 amino acids. d) Sequence analysis of the junction between the T-DNA and MRE11 gene obtained via sequencing in the mre11-4 mutants. The top line shows the genomic sequence, exon sequence is shown in uppercase letters, intron sequence is shown in lowercase italic letters, the filler DNA nucleotides are shown in small red uppercase letters and the nucleotides derived from the T-DNA insertion are shown in uppercase boldface letters. The bottom lines show the predicted amino acid sequence as a result of the T-DNA insertion. If the truncated intron 18 is not spliced out, hypothetically, 35 amino acids (ARRYRFS CLITFFNSGLLFQTGTTLNPFSGYSFDL) could be derived from the intron, filler DNA and T-DNA and form the C terminus of the predicted protein in the mre11-4 line. The predicted STOP codon is indicated by *.