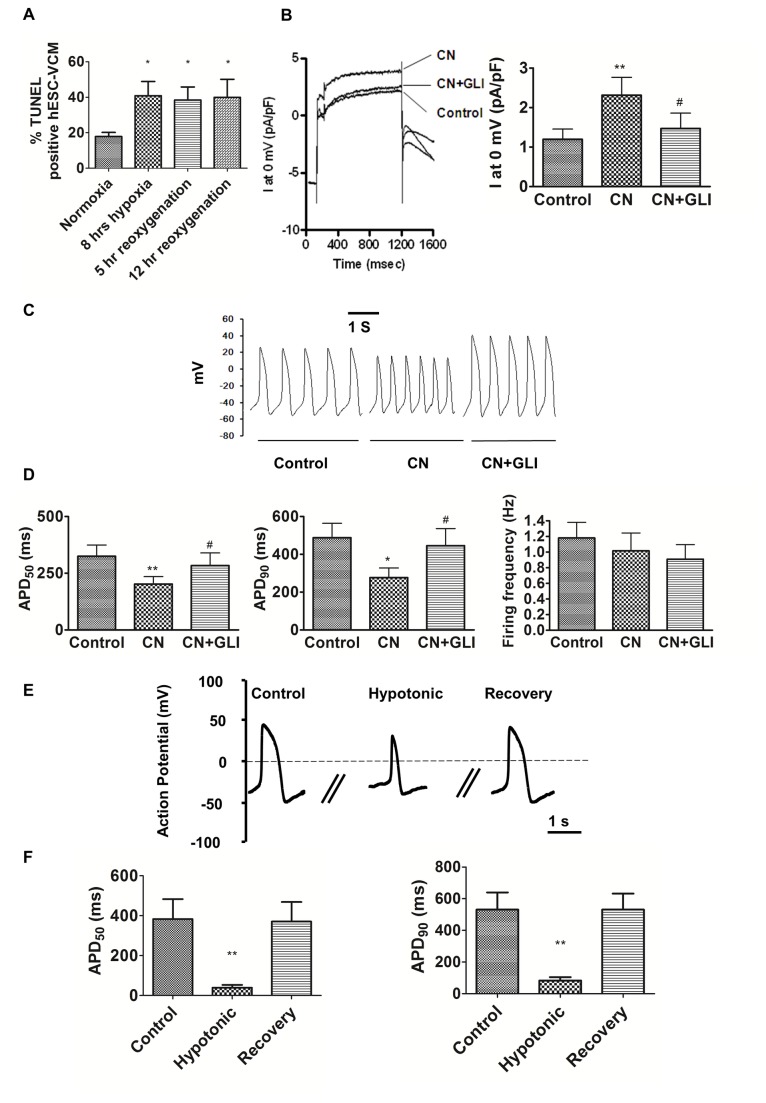
Figure 3. Functional analyses of hESC-VCMs.
A) Apoptotic response after hypoxia/reoxygenation was assessed using TUNEL assay. HESC-VCMs were subjected to hypoxic treatment, followed by reoxygenation of different duration as indicated. *P<0.05 relative to normoxic conditions.
B) I KATP channel current and its effect on electrophysiological properties of hESC-VCMs. Representative current and summary of current densities of whole-cell patch-clamp recording of hESC-VCMs. Extracellular application of I KATP channel openers, 2 mmol/L sodium cyanide (CN), at 2 min significantly increased current densities compared to controls, which was inhibited by I KATP channel blocker 10 uM glibenclamide (GLI). Cells were stimulated to 0 mV for 1000 ms from a holding potential of -80 mV preceded by a 100-ms prepulse to -10 mV. C) Representative tracings of action potentials of hESC-VCMs before and after treatment of 2 mM CN and then 10 uM GLI. D) The effect of CN and GLI on APD50, APD90 and firing frequency. N=6; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 compared to control group; #P<0.05, compared to CN group. Effect of hypotonic insult on hESC-VCMs. E) Representative tracings of action potentials of hESC-VCMs before and after hypotonic insult, and upon recovery. F) The effect of hypotonic insult on APD50 and APD90. N=6; **P<0.01 compared to control group.