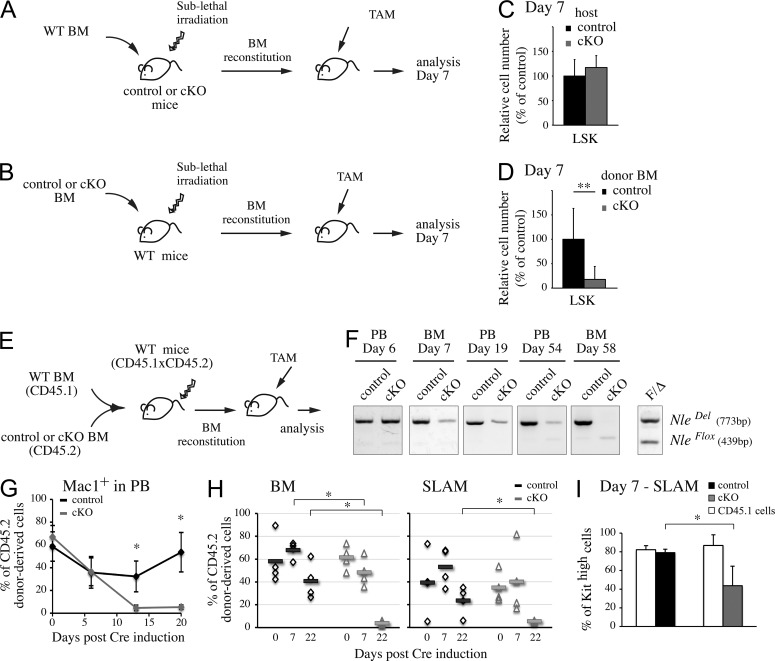
Figure 4.
Nle is required cell autonomously for HSC function. (A and B) Schematic representation of the noncompetitive transplantation strategy. Wild-type BM was transplanted into irradiated control or NlecKO mice (A) and conversely (B). After 2 mo, mice were treated with tamoxifen for 5 d. (C and D) 7 d after the first injection, the number of LSK cells in the BM of grafted mice was measured. Bars are means (SD) of n = 8–10 mice per genotype from two independent experiments. (E) Scheme of the competitive transplantation experiment. Wild-type CD45.1×CD45.2 mice were irradiated and engrafted with a mix of donor CD45.2 control or NlecKO and competitor CD45.1 wild-type BM cells (ratio 1:3 or 1:4). After 2 mo, mice were injected with tamoxifen. (F) PCR analysis on BM or PB cells from competitive chimeras at different time points after Cre induction. Similar results were obtained from three independent experiments. (G) The percentage of CD45.2 donor–derived cells among Mac1+ PB cells was measured at different time points. Depicted are the means (SD) of n = 4 mice per genotype. Similar results were obtained twice independently. (H) The percentages of CD45.2 donor–derived cells among BM or SLAM cells were measured before and at different time points after Cre induction. Similar results were obtained from three independent experiments. Individual measures and means (horizontal bars) are shown. (I) Proportion of c-Kithigh cells among SLAM cells in competitive chimeras 7 d after Cre induction. Bars are means (SD) of n = 4 mice; this experiment was performed three times. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.005.