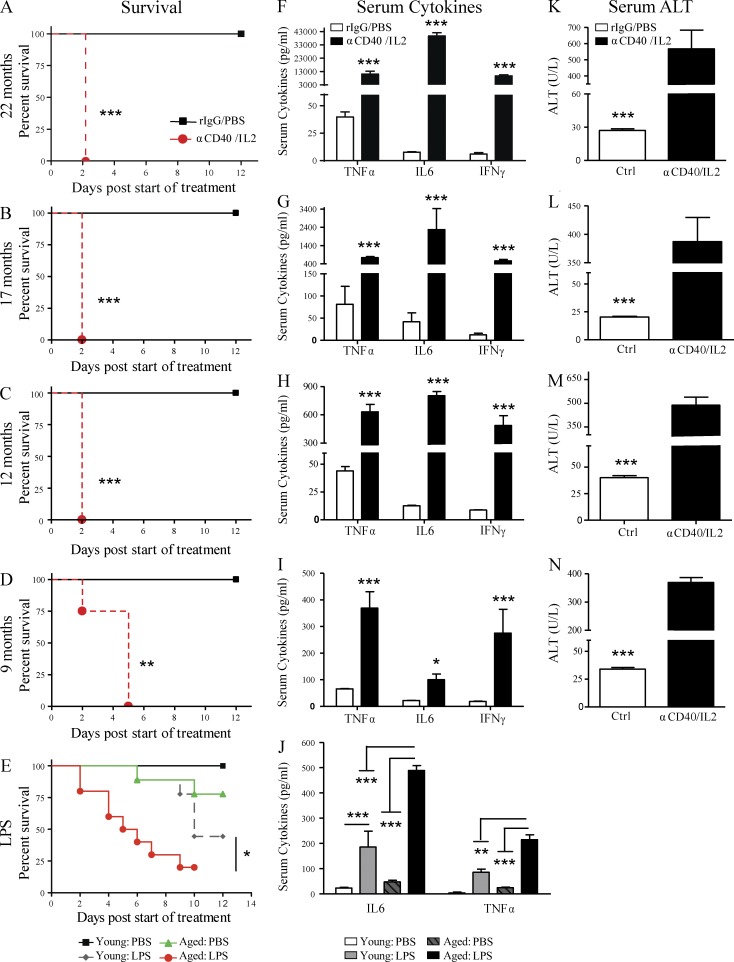
Figure 2.
Anti-CD40/IL-2 and LPS-mediated mortality and associated toxicities worsen with age. Survival of aged (A and B; 22 and 17 mo) and middle-aged (C and D; 9 and 12 mo) C57BL/6 mice after high-dose anti-CD40/IL-2 treatment or rIgG/PBS treatment (control). n = 5 in controls and n = 6–8 in anti-CD40/IL-2. (E) Survival of young (2–4 mo) or aged (17–18 mo) BALB/c mice that received 1.5 mg/kg LPS or PBS on day 0, n = 9–10. (F–I) Serum collected from mice of the same age and treatment regimen as in A–D was quantified for TNF, IL-6, and IFN-γ levels. (J) Serum IL-6 and TNF was assessed in young (4 mo) or aged (17–18 mo) mice from 48 h (E) after in vivo PBS or LPS treatment. (K–N) Serum ALT levels (measure of liver necrosis) from mice of F–I. A–D, F–I, and K–N are representative of four independent experiments, and E and J are representative of three independent experiments. Survival analysis was plotted according to the Kaplan-Meier method, and statistical differences were determined with the log-rank test. Bar graph (mean ± SEM) statistics were determined by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post-tests. ***, P < 0.001; **, P < 0.01; *, P < 0.05. Ctrl: control.