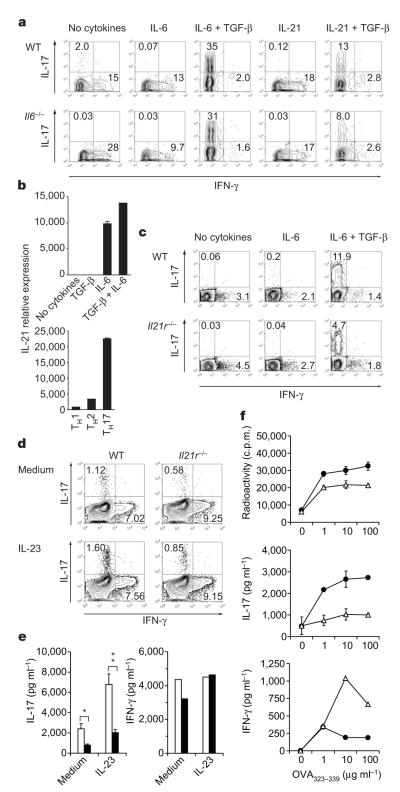
Figure 4. IL-21-driven TH17 differentiation is independent of IL-6.
Naive (a, b), total (c) or CD44+CD4+ T cells (d, e) were cultured with anti-CD3 plus corresponding irradiated antigen-presenting cells (a, c) or anti-CD3 plus anti-CD28 (b, d, e) and the indicated cytokines. a, c, Percentages of IL-17+ and IFN-γ+ cells in T cells from wild-type (WT) or Il6−/− mice (a) and WT or Il21r−/− mice (c) after four days of culture. b, IL-21 mRNA was determined by quantitative RT–PCR (means and s.e.m. for duplicate determinations). d, e, CD4+CD44+ T cells from WT or Il21r−/− mice were stimulated with or without recombinant IL-23 for 48 h. IL-17 and IFN-γ production were determined by intracellular cytokine staining (d) and ELISA (e; open columns, WT; filled columns, Il21r−/−) (asterisk, P < 0.0005; two asterisks, P < 0.003; t-test). f, WT (filled circles) and Il21r−/− (open triangles) mice were immunized with ovalbumin 323–339 peptide (OVA323–339)/CFA. Draining lymph-node cells were assayed for antigen-specific proliferation and cytokine production (means and s.d. for triplicate cultures).