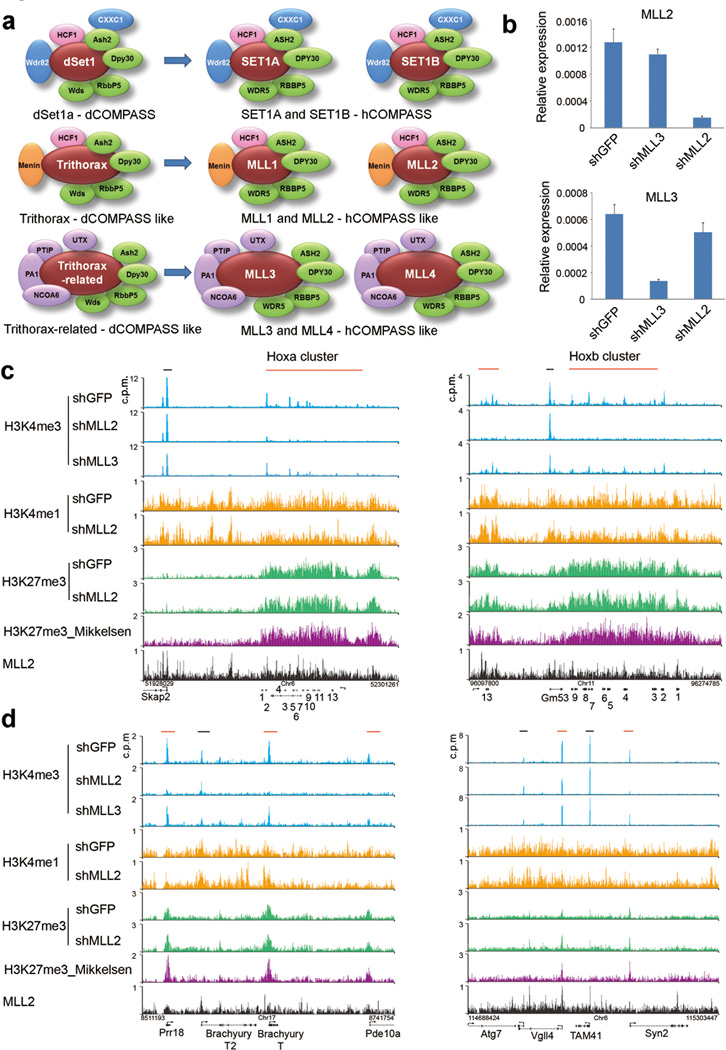
Figure 1.
Mll2 is required for the trimethylation of Histone H3 lysine 4 at bivalent homeotic genes. (a) The COMPASS family of H3K4 methylases in Drosophila (3 members on the left) and mammals (6 members, on the right). Subunits common to all COMPASS family members from yeast to human are shown in green; complex-specific subunits are shown in blue, orange and purple. (b) Mll2 and Mll3 mRNA levels after RNAi-mediated knockdown in mouse embryonic stem cells with shRNAs targeting GFP (shGFP), Mll3 (shMll3) or Mll2 (shMll2). Expression was determined by qRT-PCR and is shown relative to Actin (Actb). Results are shown as means and s.d. (n=2 technical replicates, representative of three biological replicate experiments). (c) ChIP-seq track file examples of H3K4me3 at mouse Homeobox (Hox) gene clusters. Red and black bars above the tracks indicate bivalent and non-bivalent regions, respectively. H3K27me3 data from Mikkelsen et al.4 is shown for comparison (purple). (d) ChIP-seq track examples of bivalent and non-bivalent chromatin in control and Mll2 shRNA-treated cells. Bivalently marked genes such as Prr18, Brachyury (T), Vgll4 and Syn2 are shown with red bars above the tracks as in (c).