Fig. 8.
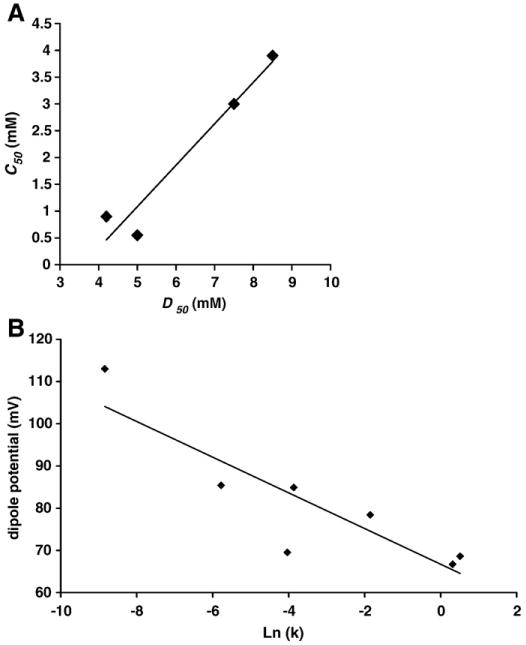
(A) Values of C50, which is the bile acid concentration at which 50% of maximal permeability to calcein was obtained, was plotted against D50, which is the bile acid concentration at which 50% of the maximal dipole potential was obtained. A linear correlation shown in the plot indicates that the change in membrane integrity and permeability is likely caused by the ability of bile acids to influence lipid orient and packing density within the membrane (r2=0.947). (B) The values of the membrane dipole potential of liposomes treated with various bile acid combinations were plotted against Ln (k), the rate of solubilization, for corresponding treatments. A linear correlation (r2=0.78) was found between the two parameters, further suggesting that the ability of bile acids to alter membrane integrity is tied to their ability to change lipid packing density.
