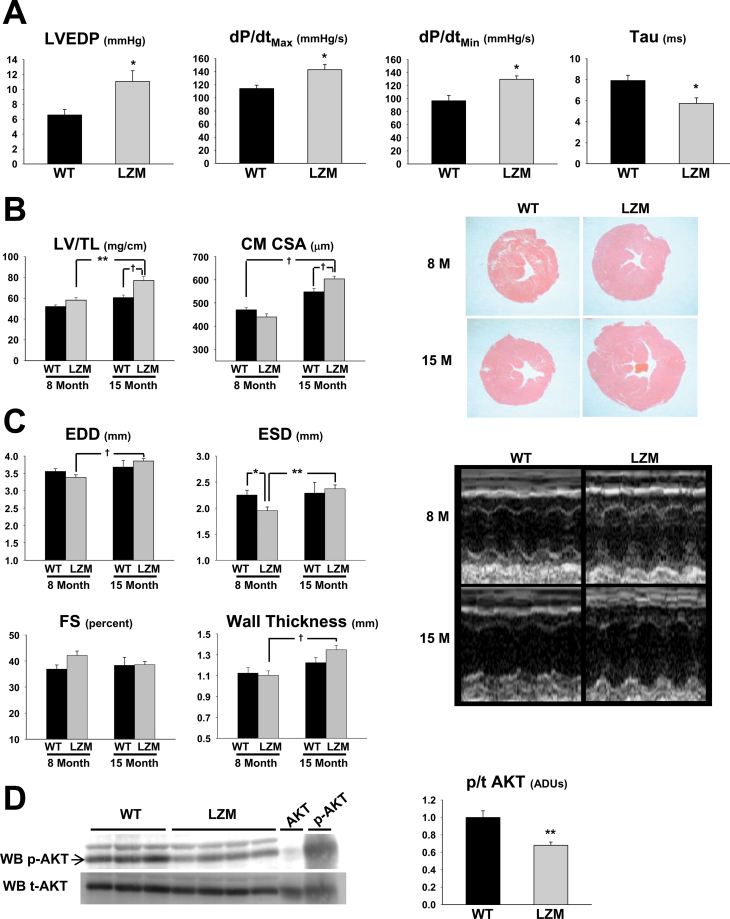
Figure 1.
Age-dependent pathological left ventricular hypertrophy in protein kinase G I alpha LZM mice. (A) Summary data of left ventricular hemodynamic measurements obtained from 8-month WT and LZM mice. n = 4 per group. (B) Summary data of left ventricular mass normalized to tibia length; representative left ventricular mass cut in cross-section at the midpapillary level and stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin; and left ventricular cardiac myocyte cross-sectional area. Summary data of WT and LZM mice at 8 and 15 months of age. n = 11 WT, 9 LZM 8 month, 5 WT, and 13 LZM 14 month; n > 120 myocytes in each experimental group. (C) Summary data and representative images of left ventricle echocardiography from WT and LZM mice at 8 and 15 months of age. (D) Immunoblot of phospho- and total AKT from left ventricles of WT and LZM 12-month-old mice. AKT and p-AKT, positive controls for total and phosphorylated AKT, respectively. n = 3 WT, 4 LZM. LVEDP = left ventricular end-diastolic pressure; LV dP/dt Max = peak rate of LV pressure rise; LV dP/dt Min = peak rate of LV pressure decline; Tau = time constant of LV relaxation; LV/TL = left ventricular mass normalized to tibia length; CSA = cross-sectional area; EDD = left ventricular end-diastolic dimension; ESD = left ventricular end-systolic dimension; FS = left ventricular percent fractional shortening; WB = Western blot; ADU = arbitrary densitometric unit; LSM = leucine zipper mutant; WT = wild type. *p < .05; **p < .01; † p < .001.