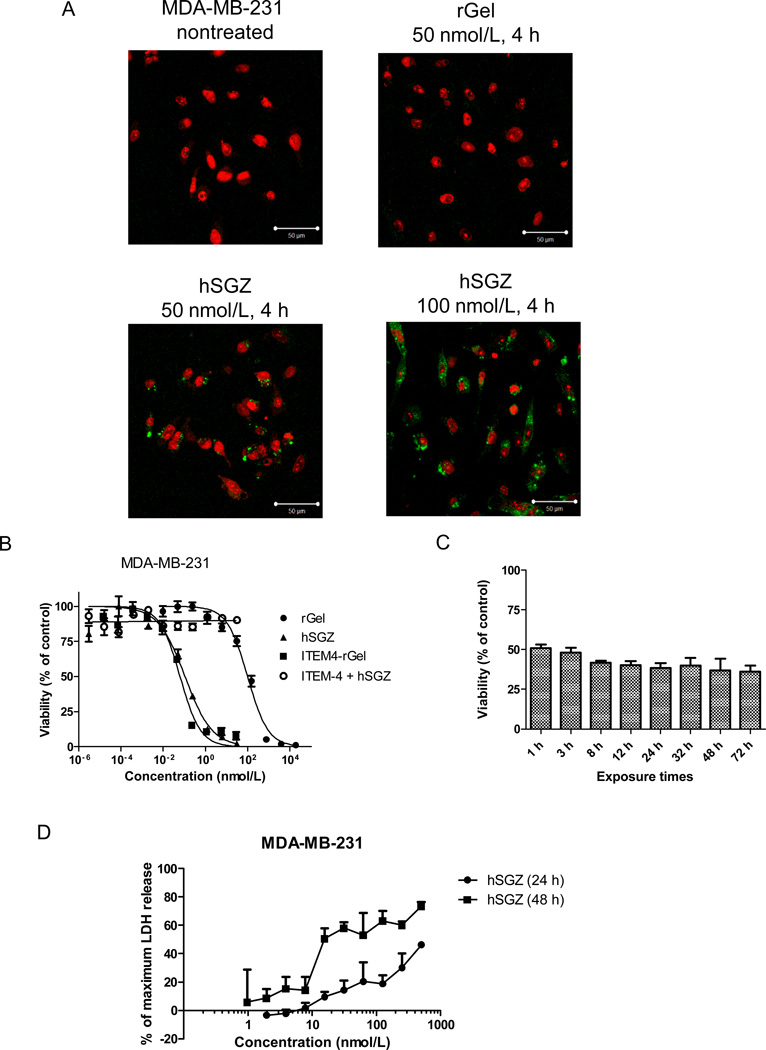
Figure 1.
Effect of the humanized, dimeric single-chain immunotoxin hSGZ on MDA-MB-231 cells. A, cells with either left untreated or treated with 50 nmol/L rGel and 50 or 100 nmol/L hSGZ for 4 h. The cells were fixed, acid washed to remove surface-bound material, permeabilized, and immunostained for the presence of rGel (green). The cells were counterstained with propidium iodide (red) to identify nuclei and visualized using a confocal microscope. Bar=50 µm. B, cells were treated with indicated concentration of rGel, ITEM4-rGel or hSGZ for 72 h. Additionally, cells were pretreated with 1 µmol/L ITEM-4 for 2 h and then coincubated with different concentration of hSGZ for another 72 h. Cell viability was assessed by crystal violet staining. C, cells were plated and then exposed to hSGZ at 0.3 nmol/L for indicated periods of time. Cell viability was assessed at 72 h as described above. D, cells were treated with different concentrations of hSGZ for 24 or 48 h and LDH release was measured. Treatment of cells with Triton X-100 served as a positive control causing maximum LDH release. Results represent mean ± SD, n = 3.