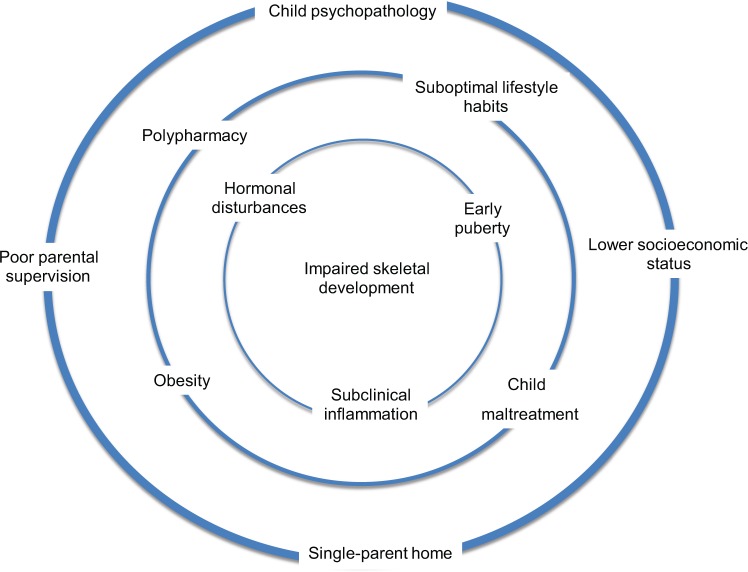
Figure 2.
Psychotropic treatment, particularly the use of antipsychotics, is associated with a multitude of factors that might, directly or indirectly, impair bone development in children and adolescents. For instance, childhood psychopathology may be associated with suboptimal lifestyle habits, hormonal changes (e.g. hypercortisolemia), and the concurrent use of several medications that may affect bone metabolism.