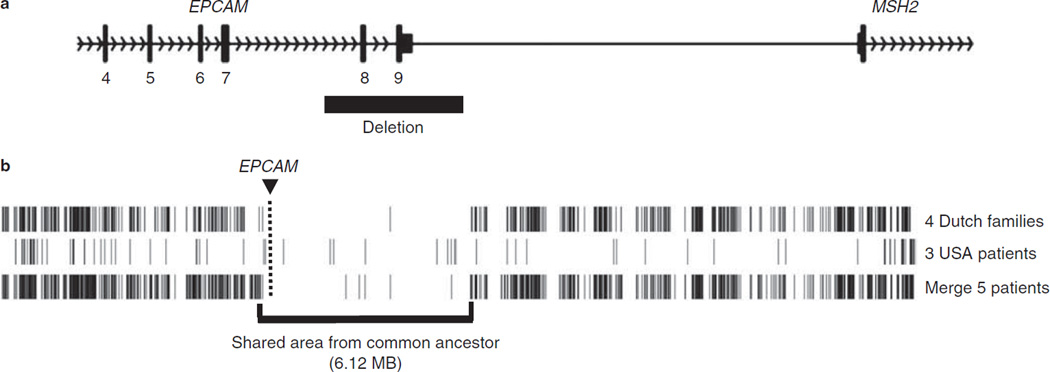
Figure 3.
EPCAM founder mutation. (a) Schematic representation of the epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EPCAM) founder deletion seen in Families A and R. The deletion encompasses exons 8 and 9 of the EPCAM gene but does not extend into the MSH2 promoter. (b) Representation of Affymetrix SNP6.0 array data of the genomic region around EPCAM in four Dutch Families (including Family A) and three members of USA Family R. Haplotypes of chromosome 2 were derived from homozygous calls of the 75,933 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) on this chromosome, and positions of discordant homozygous calls (DHCs) were marked. The location of EPCAM is indicated by the box and line. For Family A and Family R, there is a shared region, which includes EPCAM (boxed). Comparing the Dutch family members and one member of Family R (the lane labeled “Merge 5 patients”) there is a stretch of 2,186 SNPs (6.12 Mb) with only five DHCs, strongly indicating a common ancestor. For the Dutch patients, there were two large stretches of 1,341 and 906 SNPs, without DHCs, separated by a single DHC. For Family R, there is a larger stretch of shared SNPs compared with Dutch Family A members. This stretch is 17.22 Mb, 9,850 SNPs long with 81 DHCs. The larger shared haploblock seen in Family R would be consistent with the founding of Family R in the United States by immigration of a single Dutch EPCAM mutation carrier after origination of the deletion in the Netherlands.