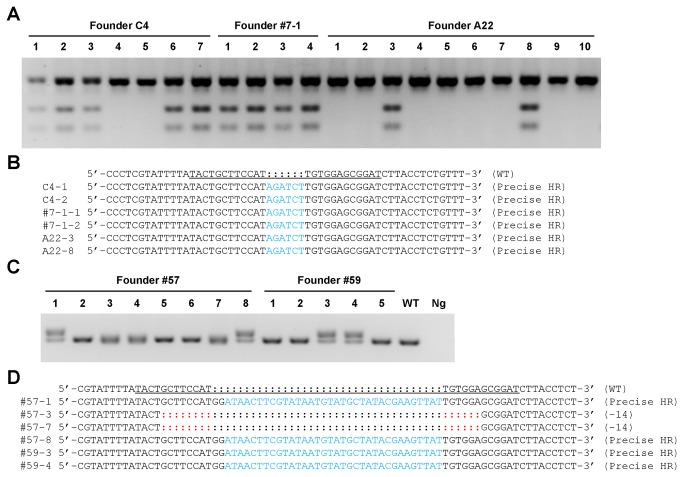
Figure 4. Germline transmission of the targeting modification.
a. The representative gel electropherogram of the genotyping result by BglII digestion of the PCR product. F1 mice derived from founders C4, #7-1, and A22 were genotyped by BglII digestion of the PCR product (592 bp) amplified from tail genomic DNA of 5-day-old pups. The PCR product from the wild type c-kit allele cannot be digested by BglII (WT), while the targeted mutant allele can be digested by BglII into two distinct fragments (238 bp and 354 bp). The PCR primers are listed in Table S1.
b. Sequence analysis of the BglII restriction site insertion. The F1 mice 1 & 2 from founder C4, #1 & 2 from founder 7-1, and #3 & 8 from founder A22 were selected for sequence analysis to confirm precise restrict site insertion. ZFN binding site is underlined. BglII sites are highlighted in blue. WT, wild type.
c. The representative gel electropherogram of the genotyping results by PCR amplification. A total of 13 F1 mice from founder 57 & 59 with loxP integration were genotyped by PCR amplification using tail genomic DNA from 5-day-old pups. The expected wild type (WT) band is 178 bp, while the expected mutant band is 214 bp. The PCR primers are listed in Table S1. Ng, negative control.
d. Sequence analysis of the mutant c-kit allele of the F1 mice 1, 3, 7, and 8 from founder 57, and #3 & 4 from founder 59. The targeted region of the mouse c-kit locus was PCR-amplified from tail genomic DNA of 5-day-old founders and subjected to sequencing. Precise loxP integration was detected in F1 mice 1 & 3 from founder 57, 3 & 4 from founder 59. ZFN binding site is underlined. loxP sites are highlighted in blue. Deletions are highlighted in red. WT, wild type.