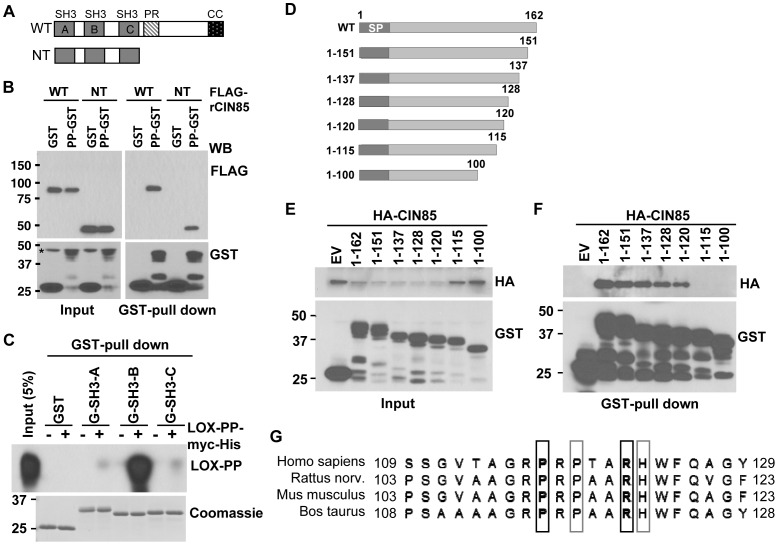
Figure 3. The SH3-B domain of CIN85 interacts with the LOX-PP region preceding aa 120.
(A) Schematic representation of the full length CIN85 (WT) and the amino terminal-containing deletion mutant (NT). The SH3, Src homology 3 domains A, B, and C, PR, proline-rich region, CC, coiled-coil domain are indicated. (B) GST or LOX-PP-GST (PP-GST) protein was co-expressed with FLAG-tagged CIN85 WT or CIN85 NT in HEK293T cells. GST-pull down assays were performed and bound or whole cell extracts subjected to WB with FLAG and GST antibodies. (C) Recombinant LOX-PP-myc-His (0.5 µM) was incubated with GST, GST (G-)-tagged SH3-A, SH3-B or SH3-C peptides (0.5 µM each) and subjected to a GST-pull down assay. The precipitated proteins were analyzed by Coomassie staining (lower panel) and with antibodies against LOX-PP (upper panel). (D) Schematic representation of LOX-PP deletion mutants prepared in the pcDNA3-GST vector. SP, Signal peptide. The lengths of the constructs are indicated on the left. (E–F) HA-CIN85 was co-transfected with either LOX-PP-WT (1-162) or the indicated deletion mutants (from part D) or empty vector (EV) DNA into HEK293T cells. Extracts were prepared and samples (4%) were analyzed directly as a measure of input (E) or subjected to GST-pull down assays and WB for HA and GST (F). (G) Amino acid sequences of LOX-PP from various species are shown. The positions of aa 111 and aa 116 and of aa 113 and aa 117 are indicated by black and grey boxes, respectively.