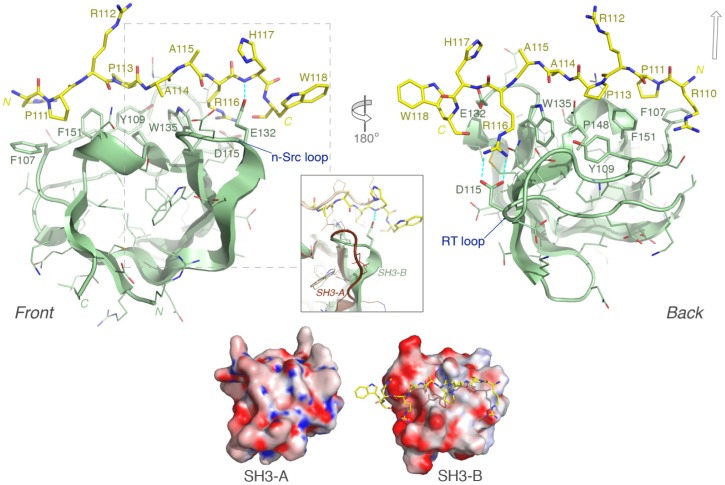
Figure 5. Structural model of CIN85 SH3-B domain in complex with the LOX-PP peptide. Upper part:
Front and rear views of the modeled SH3-B (pale green) and LOX-PP (yellow sticks) complex are depicted; selected, key electrostatic interactions are represented by blue dashed lines. The open arrow (upper right) indicates the approximate position of Arg(-2) in structures that can assemble the ternary complex: SH3–[RxP1xxxxR/K peptide]–SH3. Inset box: Detail showing the structural dissimilarity in the n-Src loop between CIN85 SH3-B (our model) and SH3-A, superimposed (PDB code: 2BZ8; brown cartoon). In the SH3-A structure, the bound Cbl-b peptide backbone (light brown) is also seen to diverge more towards its C-terminus from the LOX-PP peptide position. Lower part : Comparison of the electrostatic potential surfaces of SH3 domains A and B in equivalent orientations, illustrating their differential charge distributions. The Adaptive Poisson-Boltzmann Solver (APBS) software [55] was used to generate the electrostatic potential map, contoured in varying colour intensity from -15 (red) through 0 (white) to +15 (blue) kT/e, and rendered within PyMOL (www.pymol.org).