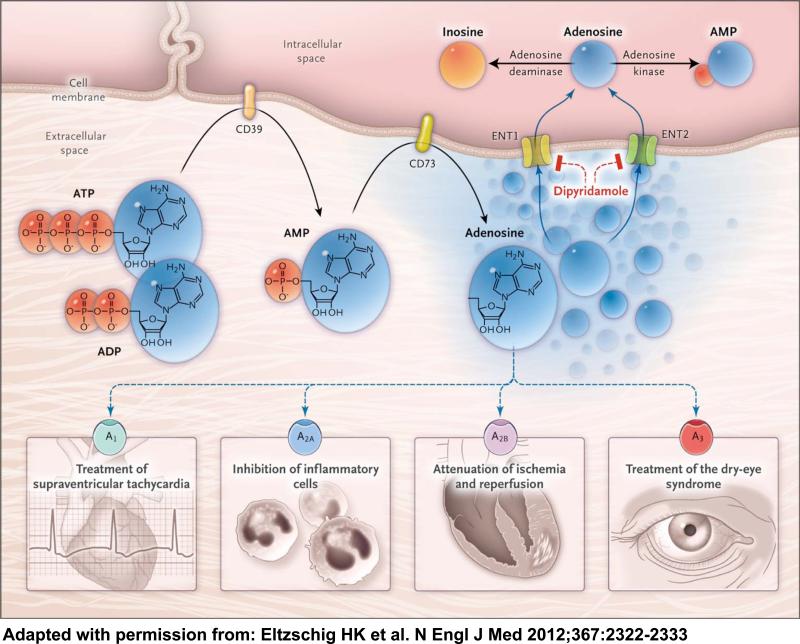
Figure 1. Extracellular adenosine signaling.
Extracellular adenosine is generated from enzymatic conversion of the precursor nucleotides ATP and ADP to AMP through the enzymatic activity of the ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 1 (CD39) and the subsequent conversion of AMP to adenosine through ecto-5′-nucleotidase (CD73). Extracellular adenosine can signal through four distinct adenosine receptors: ADORA1 (A1), ADORA2A (A2A), ADORA2B (A2B), and ADORA3 (A3). Adapted from the New England Journal of Medicine with permission.