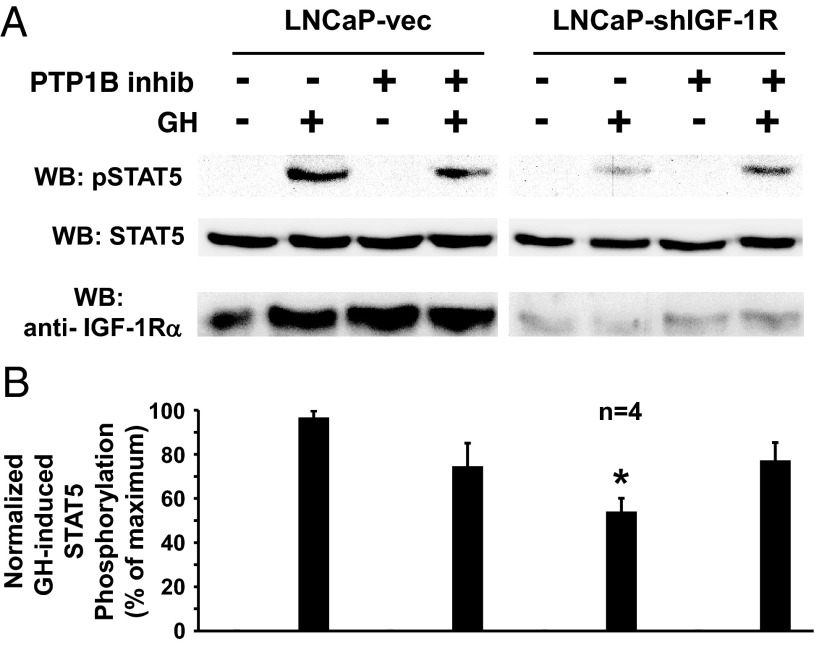
Figure 4.
A PTP-1B inhibitor reverses the diminished GH-induced STAT5 phosphorylation resulting from IGF-1R silencing in LNCaP cells. A and B, Serum-starved LNCaP-vec and LNCaP-shIGF-1R cells were treated with (+) or without (−) the PTP-1B inhibitor, 3-(3,5-dibromo-4-hydroxy-benzoyl)-2-ethyl-benzofuran-6-sulfonicacid-(4-(thiazol-2-ylsulfamyl)-phenyl)-amide (10 μM; 1 hour) and then with GH (+; 250 ng/mL) or vehicle (−) for 10 minutes. Detergent cell extracts were resolved by SDS-PAGE and serially immunoblotted with anti-pSTAT5, anti-STAT5, and anti-IGF-1Rα. A, Representative immunoblots. WB, Western blotting. B, Densitometric quantitation of pSTAT5/STAT5 signals from GH-treated samples from four independent experiments (including that shown in A). In each experiment, the maximum signal was considered 100%. Data are plotted as mean ± SE. *, P < .01 for comparison of LNCaP-shIGF-1R, non-PTP-1B inhibitor-treated, GH-treated group with either the LNCaP-vec, non-PTP-1B inhibitor-treated, GH-treated group or the LNCaP-shIGF-1R, PTP-1B inhibitor-treated, GH-treated group.