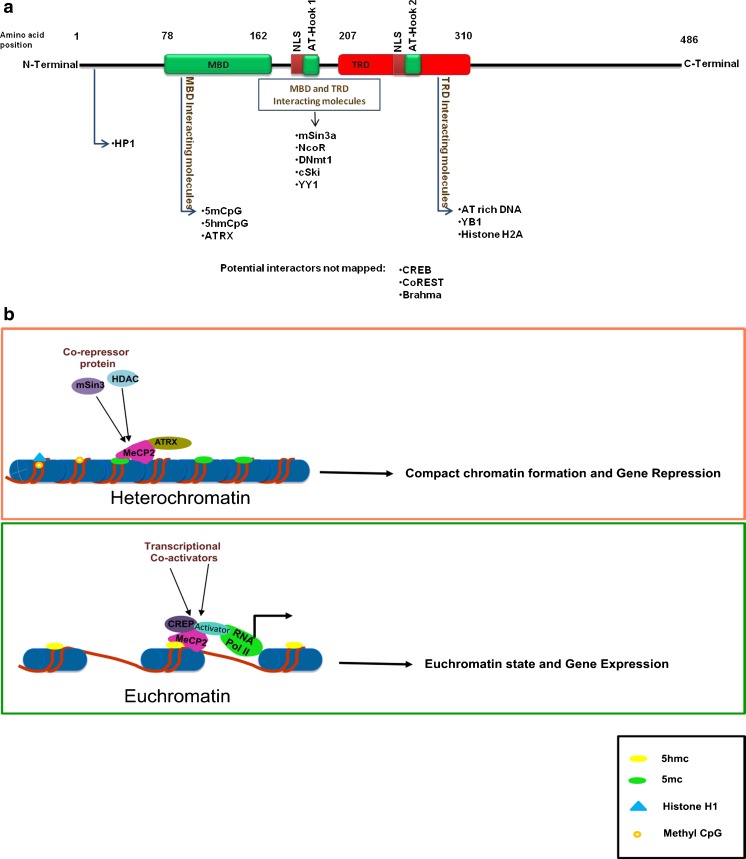
Fig. 3.
a Schematic diagram of MeCP2 domain structure and protein interactions. mCpG binding domain (MBD) [amino acids (aa) 78–162]; transcriptional repression domain (TRD) (aa 207–310) the transcription repressor domain. There are 2 nuclear localization signals (NLS), 1 between the MBD and TRD, and the other within the TRD. Three AT-hook domains have been identified: AT-hook 1 (aa 185–194), AT-hook 2 (aa 265–272) in TRD domain, and AT-hook 3 in the C-terminus. Many factors interact with these MeCP2 domains mediating specific MeCP2 functions like chromatin structure modulation, gene activation, and gene repression. b Model of the dual role of MeCp2 as a transcriptional repressor and activator. MeCp2 competes with histone H1 for sites within linker DNA resulting in a heterochromatin structure and transcriptional repression. In this process, MeCP2 interacts with 5mC = 5-methylcytosine and ATRX = alpha thalassemia / mental retardation X-linked through its MDB domain, while the AT-hook domain in the TRD interacts with AT-rich DNA. MeCP2 bound to 5mC recruits transcription repressors and co-repressors [mSin3, histone deacetylase (HDAC)] resulting in transcriptional down-regulation. When MeCP2 binds hydroxymethyl cytosine (5hmC), it recruits transcription co-activators such as cycline adenosine monophosphate response element-binding protein (CREB), to activate target gene transcription. 5mCpG = 5-methyl cytosine phospho guanosine; coREST = corepressor of REST (RE1 silencing transcription factor); CREB = cAMP response element-binding protein; RNA Pol II = RNA polymerase II