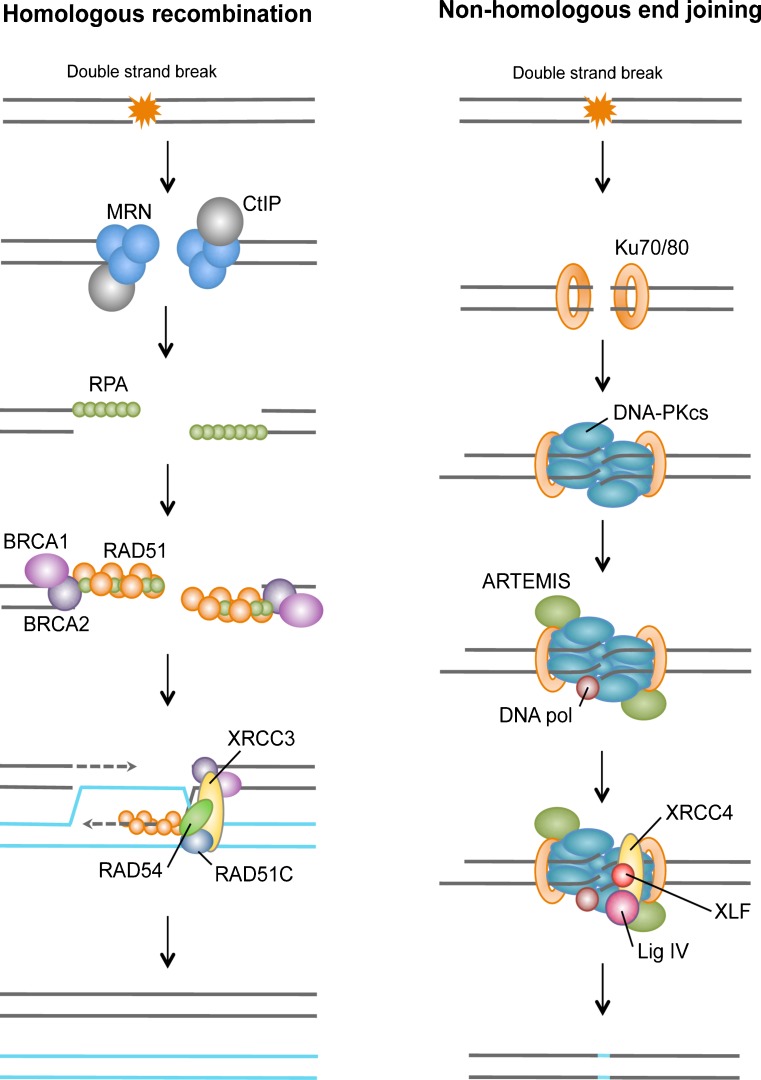
Fig. 2.
Double-strand breaks repair pathways. During homologous recombination, the repair of DSB is initiated by the resection of the DNA ends through the combined action of the MRN complex and CtIP to generate single-stranded DNA. The single-stranded ends are bound by replication protein A (RPA), BRCA1, BRCA2, RAD51 and its homologs, and can subsequently invade the homologous template. In subsequent steps, a Holliday junction is generated to prime DNA synthesis and restore genetic information that was disrupted by the DSB. During non-homologous end joining, the DSB is sensed by the Ku80–Ku70 heterodimer, which in turn recruits the DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit DNAPKcs, resulting in assembly of the DNAPK complex and activation of its kinase activity (see the figure; left panel). DNAPK increases the recruitment of Artemis, XRCC4, DNA ligase IV, and XLF, which carry out the final rejoining reaction. In many cases, NHEJ may also require the actions of a DNA polymerase(s).