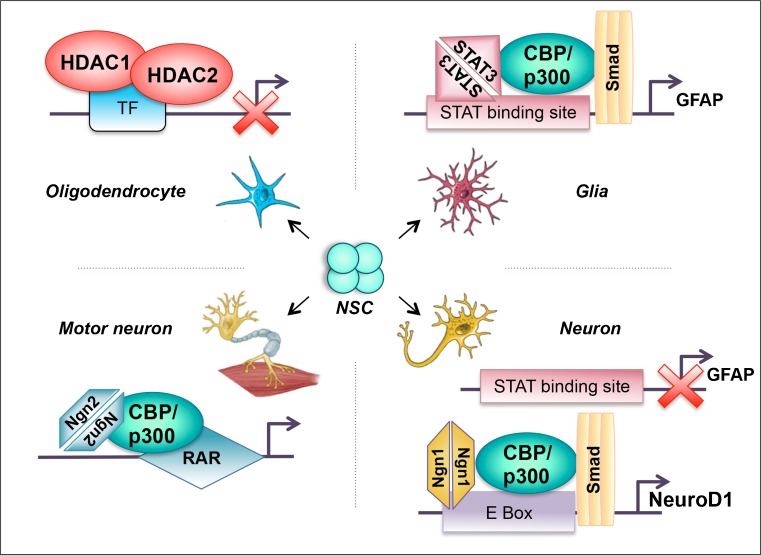
Fig. 2.
Role of acetylation in different lineage determination. The neural stem cells (NSCs) exist in a niche, which can be differentially modulated to specific neuronal lineages. A differential recruitment of specific transcription factors (TF) to the same acetyltransferases determine specific neural cell fates from the NSCs. Cyclic adenomonophosphate response element-binding (CREB) binding protein (CBP)/p300 histone acetyletransferases (HATs) interact with STAT and SMAD activating glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) expression, thus specifying the glial lineage. Increased expression of neurogenin (Ngn1) titrates this complex, thus leading to the release of STAT, blocking GFAP expression. The new Ngn1–CBP/p300–SMAD complex subsequently binds to the E box elements, which results in a neuron cell type due to the activation of NeuroD1 expression [53]. CBP/p300 when bound to retinoic acid receptor (RAR) and neurogenin 2 (Ngn2) leads to a differentiation of the motor neuron cells. The deacetylases histone deacetylases (HDACs) HDAC1 and HDAC2 act as a general repressor, blocking the transcription factor and thereby resulting in oligodendrocyte specification