Figure 1. Role of OX40 signaling in polarization of naive CD4+ T cells in vitro.
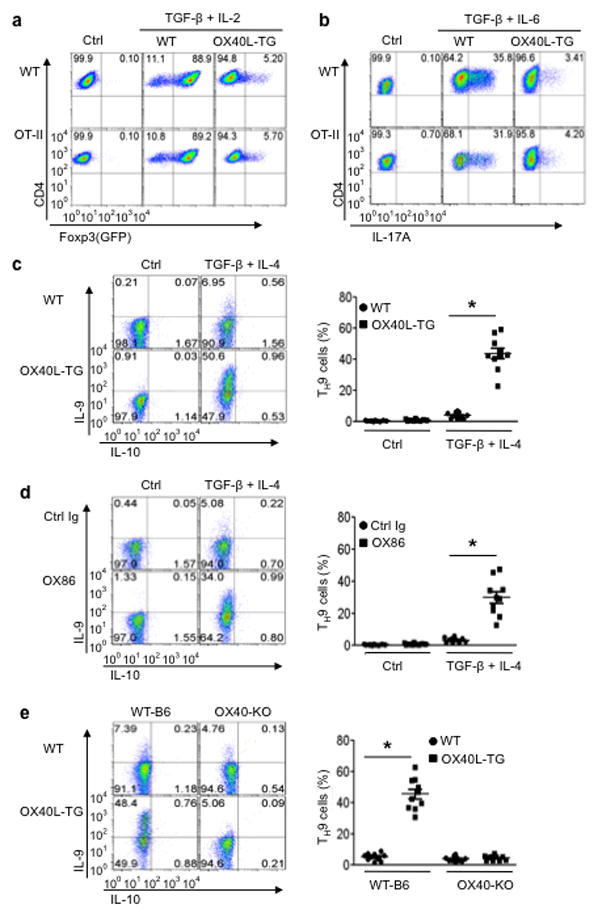
Naive CD4+ T cells sorted from WTB6, Ox40 KO, and OT-II Foxp3gfp reporter mice were cultured under iTreg, TH17, or TH9 polarizing conditions in vitro with or without engaging OX40 signaling, and induction of iTregs, TH17, and TH9 cells on day 3 was shown. (a) Induction of iTregs under polyclonal (anti-CD3) and antigen-specific settings (OVA323–339) in which WT APCs (WT) and OX40L-tg APCs (OX40L-TG) were used to activateCD4+ T cells. CD4+ T cells cultured without polarizing cytokines were included as controls (Ctrl). Numbers in quadrants denote the relative percentage of cells. The plot shown is a representative plot of 5 independent experiments. (b)Induction of TH17 cells under polyclonal and antigen-specific settings as described above. Numbers in quadrants denote the percentage of cells. The plot shown is a representative plot of 5 independent experiments. (c) Induction of TH9 cells from naïve B6 CD4+ T cells stimulated with anti-CD3+ WT APCs (WT) or OX40L-tg APCs (OX40L-TG). The panel on the right is a summary of all experiments performed and the dots denote individual experiments (n=10). (d)Naive CD4+ T cells were activated with anti-CD3plus WTAPCs with or without an agonist anti-OX40 mAb (OX86), and induction of TH9 cells was shown. The panel on the right is a summary of individual experiments (n=10). (e) Naïve B6 and Ox40 KO CD4+ T cells were activated with anti-CD3and APCs under TH9-polarizing conditions, and induction of IL-9 producing cells was shown. The panel on the rights is a summary of all experiments (n=10). * p <0.05.
