Figure 6. Role of the non-canonical NF-kB pathway in OX40-mediated induction of TH9 cells.
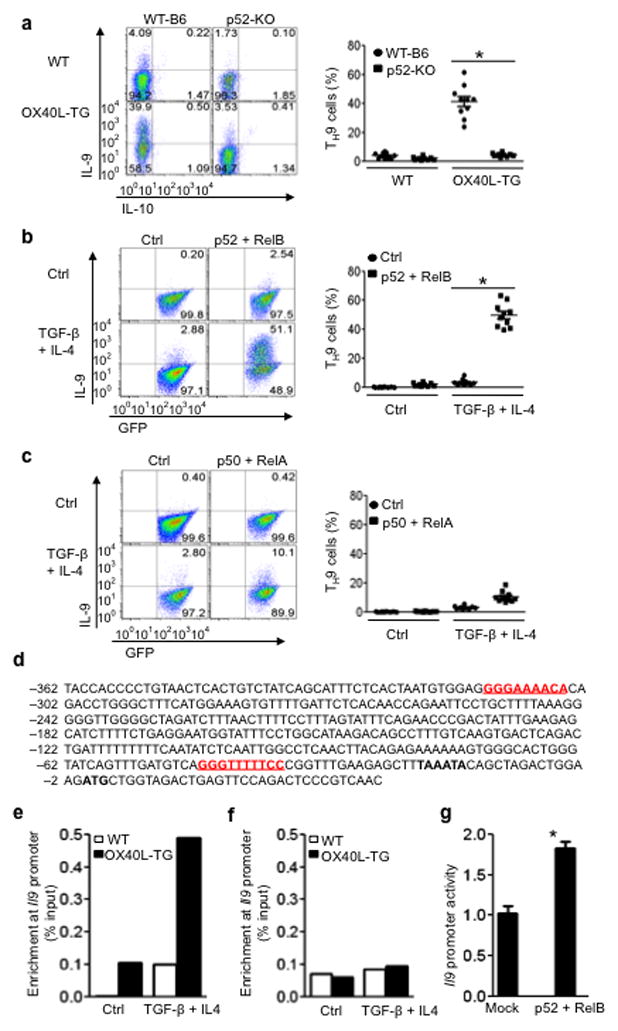
(a) WT-B6 and p52-KO CD4+ T cells were activated with anti-CD3 plus WT APCs (WT) or OX40Ltg APCs (OX40L-TG) under TH9 polarizing conditions for 3 days, and induction TH9cells was shown. The panel on the right is the percentage of TH9 cells among naïve CD4+ T cells and the dots denote individual experiments (n=10). (b) Retroviral transduced WTCD4+ Tconv expressing RelB and p52 were cultured with or without TH9 polarizing cytokines for 3 days, and induction of TH9 cells was shown. The panel on the right depicts the results of all experiments (n=10). (c) WT-B6 CD4+ T cells were transduced with retroviral vectors encoding p50 and RelA, and IL-9 expression by the transduced T cells under TH9-polarizing conditions on day 3 was shown. The right panel depicts the results of all experiments (n=10). (d) Putative NF-kB binding sites in the IL-9 promoter region. The red color depicts the, and the TATA box is shown in bold font. (e) WTCD4+ T cells were activated with anti-CD3 plus either WT APCs (WT) or OX40Ltg APCs (OX40L-TG) under either neutral (Ctrl) or TH9 inducing conditions (TGF-β + IL-4), and enrichment of RelB at the IL-9 promoter region was determined by ChIP and shown. Data shown are representative of 1 of 3 independent experiments. (f) WTCD4+ T cells were cultured under either neutral or TH9 polarizing conditions, and ChIP of RelA binding to the IL-9 promoter region was shown. One of 3independent experiments is shown. (g) 293T cells were transfected with IL-9 promoter-luciferase construct with or without expression vectors encoding full-length RelB and p52. The promoter activity is presented as fold increase over cells transfected with the empty vector alone. Data are 1 of 3 independent experiments (mean ± SEM), * p<0.05.
