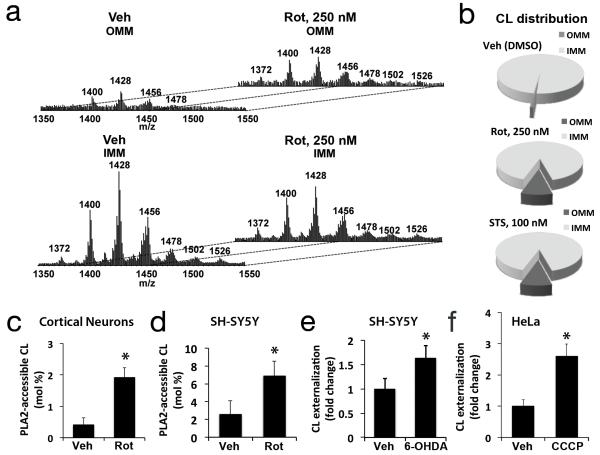
Fig. 2. Analysis of mitochondrial CL distribution and externalization.
IMM and OMM fractions isolated from primary neurons following the indicated treatments were lipid extracted for LC-MS analysis. MS spectra (a) demonstrated increased CL content of the OMM after rotenone treatment, with diversification of the cluster distribution to the 7 clusters exhibited by the IMM. Pie charts showing the CL distribution between IMM and OMM fractions from toxintreated neurons, normalized to mitochondrial lipid Pi (b). Treatment with rotenone caused significant increases in PLA2-hydrolyzable (surface accessible) CL assessed by LC-MS in primary cortical neurons (c, 250 nM) and SH-SY5Y cells (d, 1 μM). Treatment with 6-OHDA and CCCP increased surface exposure of CL probed with Annexin V in SH-SY5Y (e, 120 μM) and Parkin-expressing-HeLa cells (f, 20 μM), respectively. Mean +/− s.d. of n=3 independent experiments for c-f (see Statistics Source Data Table); * p < 0.05 vs. Control.