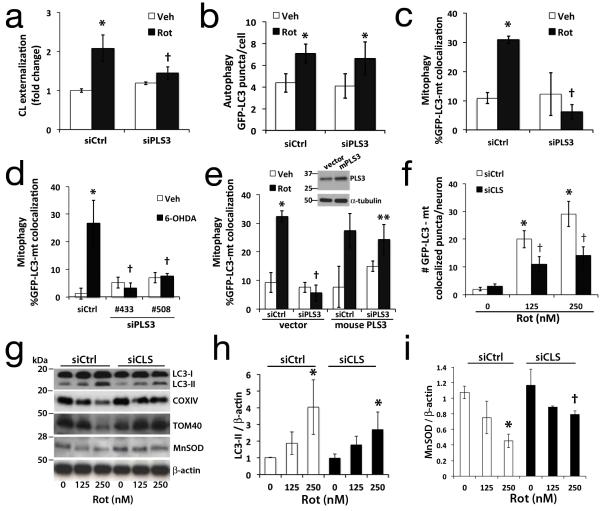
Fig. 3. RNAi knockdown of cardiolipin enzymes attenuate CL exposure and mitophagy.
SH-SY5Y cells expressing control (siCtrl) or scramblase-3 siRNA #508 (siPLS3) × 72h were stained with Mitotracker Green FM, a transmembrane potential-independent dye, and treated with rotenone (1 μM). Anionic phospholipids exposed to the outer surface of isolated mitochondria were quantified by flow cytometry for Alexa 647-annexin V binding (a). PLS3 knockdown had no effect on Rot-induced autophagy (b), but decreased mitophagy in SH-SY5Y cells treated with rotenone (c, 1 μM) or 6-OHDA (d, 120 μM). The effects of siPLS3 were recapitulated using a second siRNA #433 (d, Supplementary Fig. S3b, S3g), and reversed by transfection with an RNAi-resistant mouse PLS3 vector (e). Primary neurons transfected with cardiolipin synthase siRNA (siCLS) or scrambled siCtrl were treated with rotenone (250 nM) 72h later and analyzed for autophagy (Supplementary Fig. S1b) or mitophagy by either colocalization analysis (f), or with mitochondrial protein immunoblot (g) and densitometry (h,i; Supplementary Fig. S4c). Knockdown efficiencies are shown in Supplementary Figs. S3 & S4. Mean +/− s.d. of n=4 independent experiments for b,c, and n=3 independent experiments for a, df, h-i (see Statistics Source Data Table); * p < 0.05 vs. vehicle; † p < 0.05 vs. toxin-treated-siCtrl; ** p < 0.05 vs. Rot-siPLS3. See Supplementary Fig. S7 for uncropped blots.