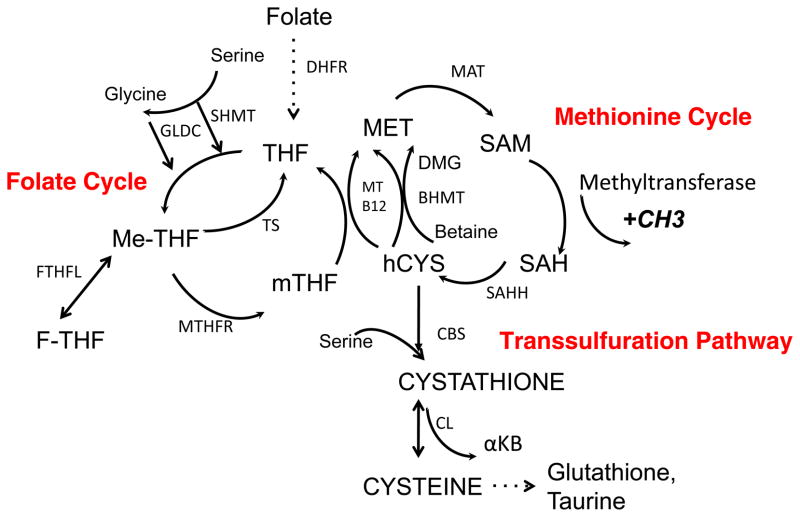
Figure 2. Folate and methionine metabolism comprise one carbon metabolism.
The folate cycle and the methionine comprise of two metabolic pathways that exist independently and thus in modules.
The folate cycle: Folate is imported in cells and reduced to tetrahydrofolate (THF). THF is converted to 5,10-methylene-THF (me-THF) by serine hydroxymethyl transferase (SHMT). Vitamin B6 appears to have an influence on this reaction but the interaction is likely indirect. This product is then either reduced to 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (mTHF) by methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) or converted to 10-Formyltetrahydrofolate (F-THF) through a sequence of steps.. mTHF is demethylated to complete the folate cycle. With the demethylation of mTHF, the carbon is donated into the methionine cycle through the methylation of homocysteine by methionine synthase and its cofactor Vitamin B12.
The methionine cycle: The methionine cycle begins with homocysteine that accepts the carbon from the folate pool through mTHF to generate methionine. Methionine, through methionine adenyltransferase (MAT) is used to generate S-adenosylmethionine (SAM), which is demethylated to form S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH). After deadenylation by S-adenosyl homocysteine hydrolase (SAHH), SAH is converted back to homocysteine resulting in a full turn of the methionine cycle.
Another modular unit of one carbon metabolism is the transsulfuration pathway. This pathway is connected to the methionine cycle through the intermediate homocysteine. Serine can condense enzymatically with homocysteine to generate cystathione by cystathionine synthase (CBS). Cystathionine is then cleaved by cystathione lyase (CGL) to generate alpha-ketobutyrate (αKB) and cysteine, which can be shunted into glutathione production and taurine metabolism. The metabolism of cysteine can also lead to its desulfhydration and production of hydrogen sulfide through CBS and CGL.
Abbreviations: SAM – S-adenosylmethionine, SAH – S-adenosylhomomocysteine, hCYS – homocysteine, THF – Tetrahydrofolate, mTHF – 5-methyltetrahydrofolate, Me-THF – 5,10 Methylenetetrahydrofolate, F-THF – 10 Formyltetrahydrofolate, DMG – Dimethylglycine, GLDC – Glycine Decarboxylase, TS – Thymidylate Synthase, MT – Methionine Synthase, B12 – Vitamin B12, MAT – Methionine adenyltransferase, SAHH – S-adenosyl homocysteine hydrolase, GNMT – Glycine N-methyltransferase, BHMT – Betaine hydroxymethyltransferase, SHMT – Serine hydroxymethyltransferase MTHFR – Methyltetrahydrofolate Reductase, DHFR –Dihydrofolate reductase, CDO – Cysteine Dioxygenase. Bi-directional arrows denote reversible steps. Dotted arrows denote multiple biochemical steps.