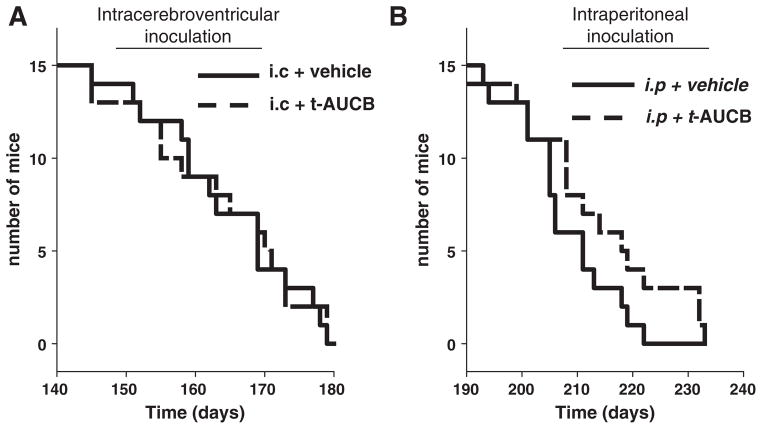
Fig. 1.
Inhibition of sEH by orally administered inhibitor delays lethality of prion infection. A) Mice inoculated by intracerebroventricular (i.c.) route and administered vehicle (PEG400, 1% in drinking water) displayed median survival time of 163 days which was not significantly different than the group receiving 1 mg/kg/day t-AUCB which had a median survival time of 165 days (log-rank test p = 0.86). B) Mice inoculated by intraperitoneal (i.p.) route and administered vehicle (PEG400, 1% in drinking water) displayed a delayed median survival time of 207 days compared to i.c. inoculation. This survival time was further delayed in the t-AUCB (1 mg/kg/day in drinking water) treatment groups which had a median survival time of 216 days (log-rank test p = 0.025).