Abstract
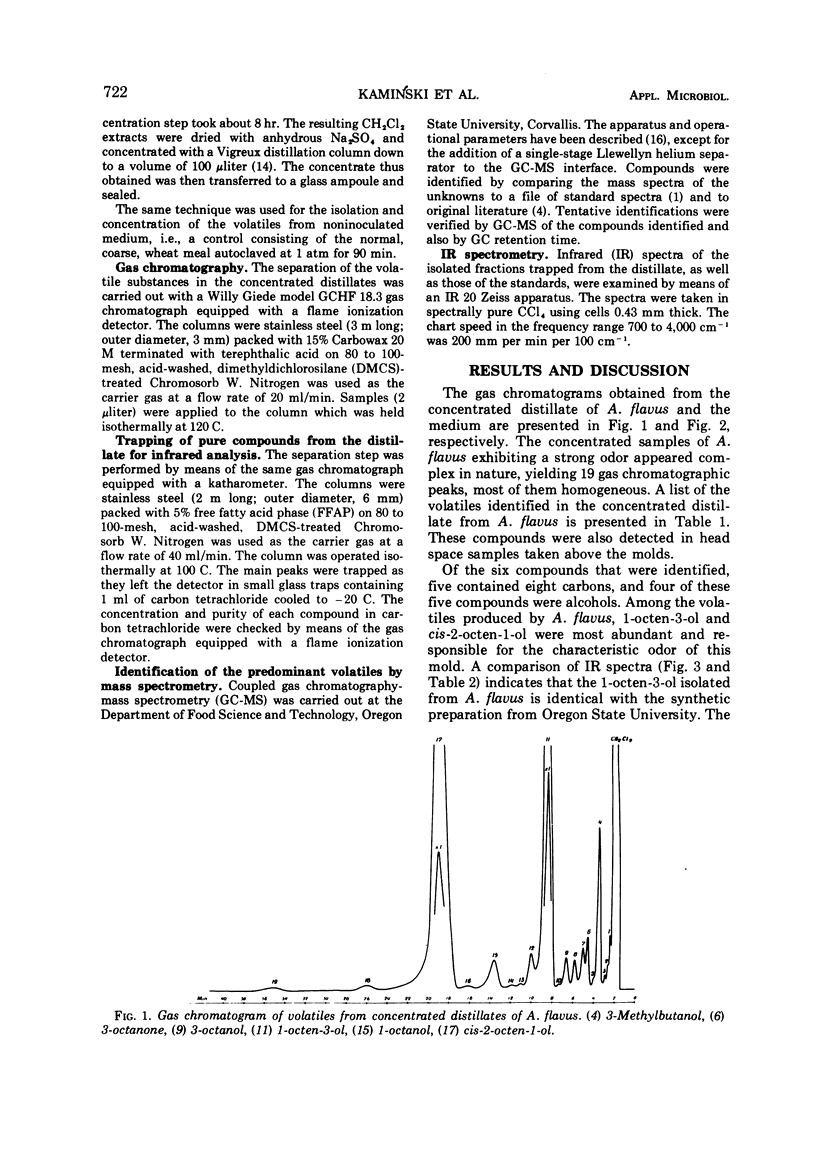
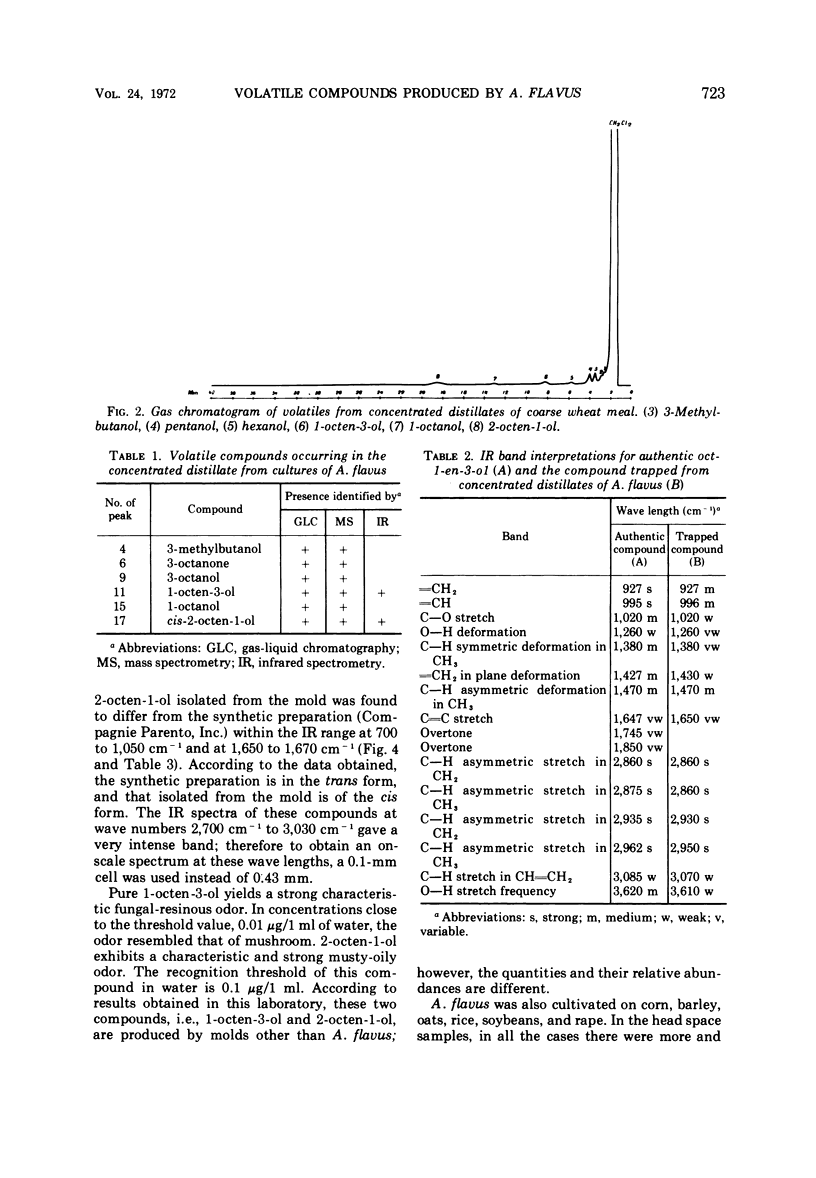
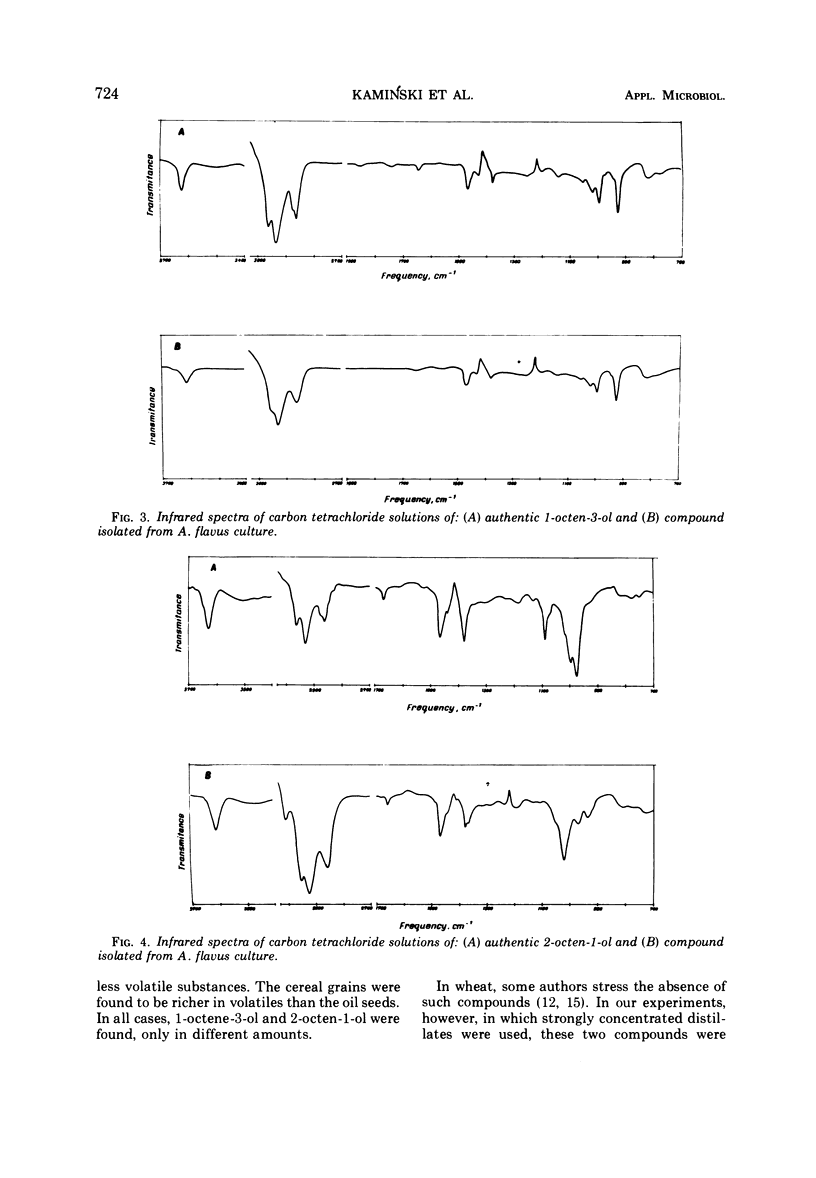
A culture of Aspergillus flavus grown on moistened wheat meal was homogenized with a blendor, and the resulting slurry was vacuum-distilled at 5 mm of Hg and 35 C. The aqueous distillate was collected in traps cooled to -10 to -80 C. The culture volatiles were extracted from the distillate with CH2Cl2, and, after removal of the bulk of the solvent, the concentrated volatiles were examined by packed-column gas chromatography. Nineteen peaks were observed, and coupled gas chromatography-mass spectrometry was employed to identify the larger components. The compounds identified were: 3-methyl-butanol, 3-octanone, 3-octanol, 1-octen-3-ol, 1-octanol, and cis-2-octen-1-ol. The two octenols were the predominant compounds, and sufficient sample was trapped from the gas chromatograph for infrared analyses; this confirmed the mass spectral identifications and permitted the assignment of the cis designation to 2-octen-1-ol. Both oct-1-en-3-ol and cis-2-octen-1-ol are thought to be responsible for the characteristic musty-fungal odor of certain fungi; the latter compound may be a useful chemical index of fungal growth.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anjou K., von Sydow E. The aroma of cranberries. II. Vaccinium macrocarpon Ait. Acta Chem Scand. 1967;21(8):2076–2082. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.21-2076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


