Fig. 1.
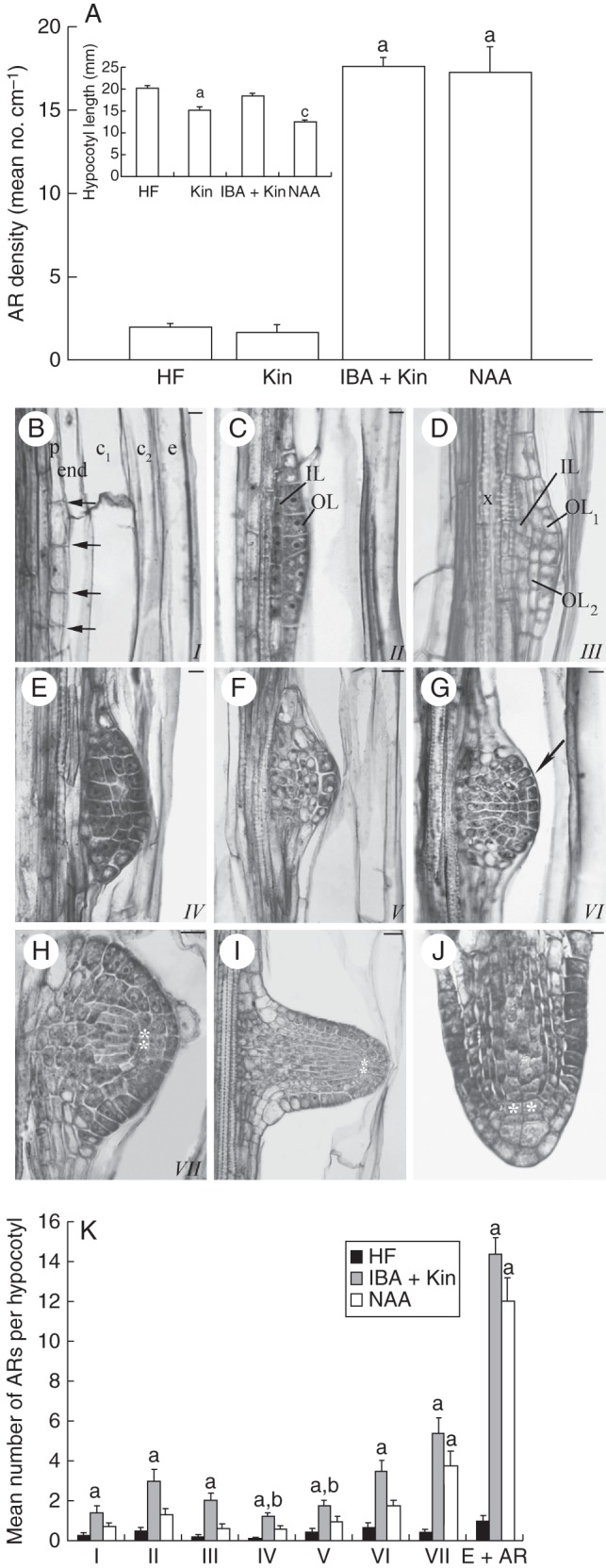
(A) AR mean density (± s.e.) in the hypocotyl of 14-day-old wild-type seedlings grown on HF, Kin (0·1 µm), IBA (10 µm) + Kin (0·1 µm) and NAA (2 µm) media, and hypocotyl mean length (inset). (B–J) Developmental stages of ARs in wild-type seedlings grown on HF medium. (B) First anticlinal divisions in the hypocotyl pericycle (arrows). (C) Outer (OL) and inner (IL) layers formed by periclinal divisions in the cells originated by the first anticlinal divisions. (D) OL periclinal doubling. (E) IL doubling, leading to a four-layered ARP. (F) ARP dome establishment. (G) ARP dome with protoderm specification (arrow). (H) Stage VII ARP showing cells with LR QC morphology (asterisks). (I) Developed ARP emerging from the hypocotyl (QC shown by the asterisks). (J) Apex of a mature AR (QC shown by the asterisks). (B–J) Histological longitudinal radial sections stained with toluidine blue (Ws ecotype). (K) Mean number (± s.e.) of ARs at different stages in wild-type seedlings grown on HF, IBA (10 µm) + Kin (0·1 µm) and NAA (2 µm) media. (A and K) a,cP < 0·01 differences from other treatments; bP < 0·05 difference between IBA + Kin and NAA. Columns with the same letter are not significantly different. n = 30 (Col ecotype). Scale bars: (B–G, J) = 10 µm; (H) = 20 µm; (I) = 30 µm. I–VII, developmental ARP stages, p, hypocotyl pericycle; x, protoxylem; c1–c2, cortex; end endodermis; e, epidermis.
