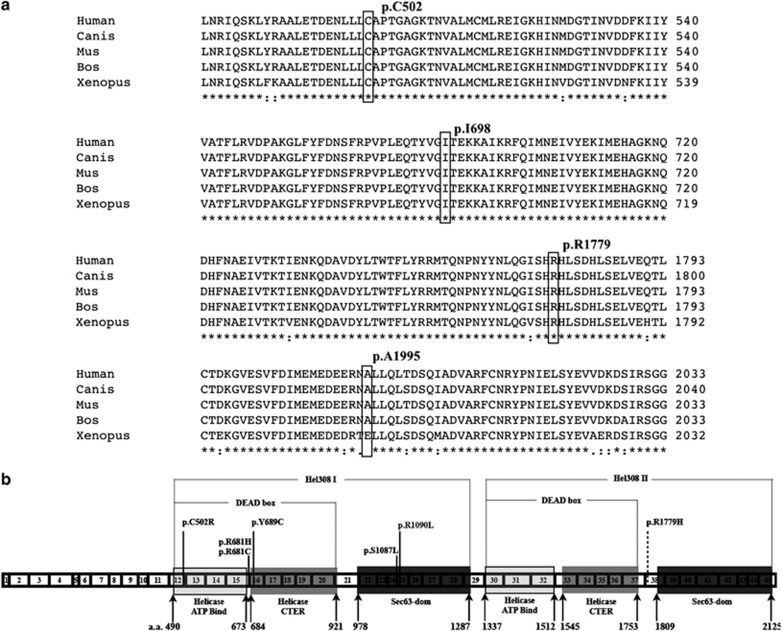
Figure 2.
(a) Multiple protein sequence alignment of SNRNP200 (partially), showing the location of p.C502, p.I698, p.R1779, and p.A1995, while the first three residues are absolutely conserved and the last residue are well conserved across different species. The accession numbers of SNRNP200 protein sequences of different species are as follows: Human NP_054733.2, Canis (Canis lupus familiaris) XP_532949.2, Mus (Mus musculus) NP_796188.2, Bos (Bos taurus) NP_001193092.1, Xenopus (Xenopus (Silurana) tropicalis) XP_002932581.1. (b) Protein structure and all reported disease-causing mutations in SNRNP200 with transcript reference No. ENST00000323853. 1–45 demonstrated exon 1–45 with corresponding length. Domain location reference software: PROSITE for helicase ATP-binding and helicase CTER domains; SMART for Sec-63 dom; a.a.: amino acid sequence number of SNRNP200; mutations reference: p.C502R (present study); p.R681H;32 p.R681C;32 p.Y689C;32 p.Q885E;33 p.S1087L;21, 32 p.R1090L;21 p.R1779H (present study, dash line indicated probably be disease causing mutation).