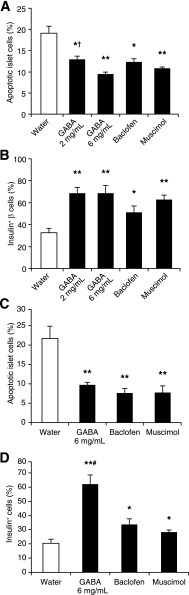
FIG. 2.
Oral GABA administration inhibits mouse and human islet cell apoptosis in vivo. C57BL/6 mice were STZ-rendered mildly hyperglycemic and given plain water or water containing GABA, baclofen, or muscimol for 48 h during which period all mice remained hyperglycemic. The percentages of apoptotic islet cells in mice were characterized by TUNEL and immunohistochemistry with anti-insulin. A: The percentages of apoptotic islet cells in hyperglycemic mice. B: The percentages of insulin+ β-cells. Mildly hyperglycemic NOD/scid mice were implanted with 2,000 human islets and treated as described in Research Design and Methods. The percentages of apoptotic islet cells were characterized using Alexa Fluor 488–based TUNEL, PE–anti-insulin, and DAPI. C: The percentages of apoptotic human islet cells. D: The percentages of human insulin+ β-cells. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM of the percentages of apoptotic islet cells or insulin+ β-cells in different groups of mice (N = 4–8 mice/group) in two independent experiments. There were no obvious inflammatory infiltrates in pancreatic islets. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. the control water group, †P < 0.05 vs. GABA 6 mg/mL, #P < 0.05 vs. baclofen and muscimol.