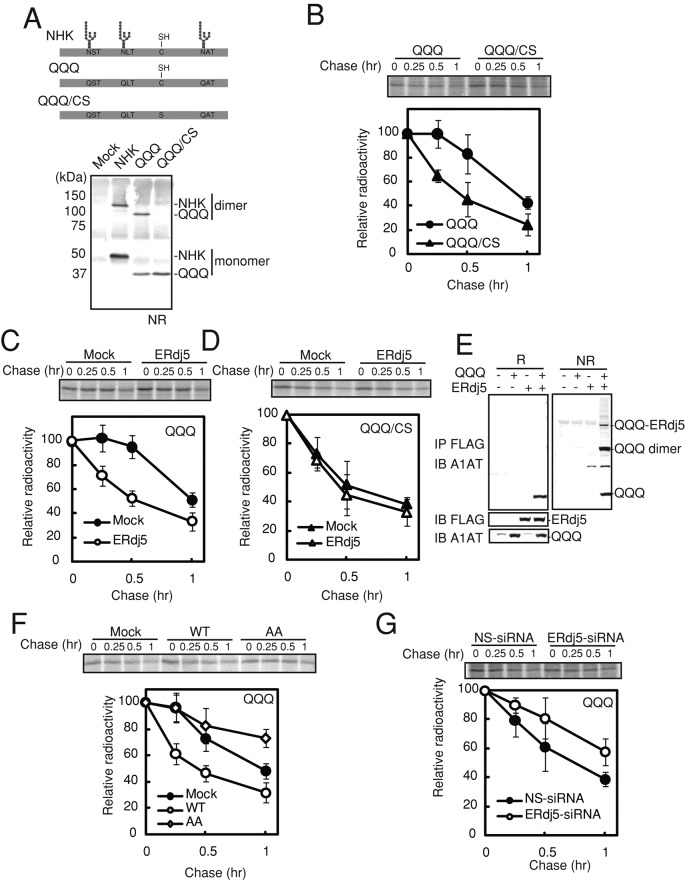
FIGURE 1:
ERdj5 accelerates ERAD of misfolded nonglycosylated proteins by cleaving their disulfide bonds. (A) Top, molecular features of wild-type, QQQ mutant, and QQQ/CS mutant NHK. The QQQ mutant lacked the three N-glycosylation sites. In the QQQ/CS mutant, a cysteine residue was replaced by serine. Bottom, nonreducing (NR) immunoblot analyses of HEK293T cells expressing wild-type and mutant NHK. (B) Twenty-four hours after transient transfection with expression plasmids containing the QQQ or QQQ/CS mutant, HEK293T cells were metabolically labeled with [35S]methionine/cysteine for 15 min and then chased for the indicated times. The QQQ and QQQ/CS mutants were immunoprecipitated with an anti-A1AT antibody. (C, D) Pulse-chase analyses of the effect of overexpression of ERdj5 on degradation of the QQQ (C) and QQQ/CS (D) mutants. (E) Twenty-four hours after the transfection of HEK293T cells with expression plasmids containing ERdj5 and the QQQ mutant, cell lysate supernatants were immunoprecipitated (IP) with an anti-FLAG antibody and then immunoblotted (IB) with anti-FLAG and anti-A1AT antibodies. NR, nonreducing condition; R, reducing condition. (F) Pulse-chase analysis of the effect of the overexpression of ERdj5/WT and ERdj5/AA on degradation of the QQQ mutant in transiently transfected HEK293T cells. (G) Effect of siRNA-induced knockdown of endogenous ERdj5 on QQQ ERAD. Pulse-chase experiments were performed 24 h after transfection of HEK293T cells with the QQQ mutant expression plasmid (72 h after transfection with either nonspecific [NS] or ERdj-5-specific siRNA). (B–D, F, G) Data represent the mean ± SD of n = 3 independent experiments.